- Windows
- Windows XP
- 23 July 2014 at 17:25 UTC
-

Partitioning a hard drive is important because it allows you to separate your data into several parts. Generally, you create at least two partitions on a hard disk.
The first partition for the operating system or OS (Windows XP in this case) and the second partition for your personal data.
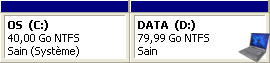
The fact to partition your hard drive in this way will you be able to format the first partition to reinstall the operating system after a crash too high of this operating system.
Before formatting the partition, you will copy the important data on the second partition and then you will format the first partition to reinstall the operating system by the installation CD/DVD
In this tutorial, we'll show you how to partition your hard drive in Windows XP.
Note : Support for Windows XP has stopped on April 8, 2014, but since many people still use it, we continue to support this OS for our tutorials.
Info : This tutorial lets you know how to partition a hard drive in Windows XP. If you want to understand how this works, refer to our article "Why and how to partition a hard drive?" who will explain the theory of partitioning.
- Initialization
- Create a single partition on the entire hard drive
- Create multiple partitions (for a Multiboot or normal use)
1. Initialization
For starters, many people are asking: "Why my new hard drive is not recognized by Windows ?".
The answer to this question is simple : The disk is not initialized. So there is no partition table or partitions. Because the workstation (or computer) only displays the partitions on your hard drives, it does not show these partitions (since there are no partitions).
Note: This problem does not happen with external hard drives because they are already initialized, partitioned (one partition on any hard drive) and format (usually NTFS).
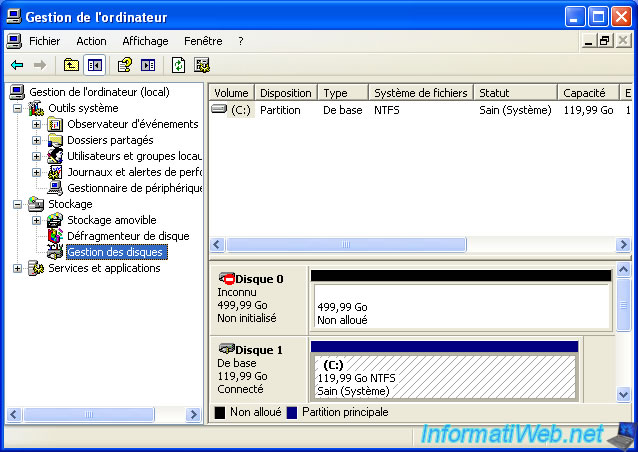
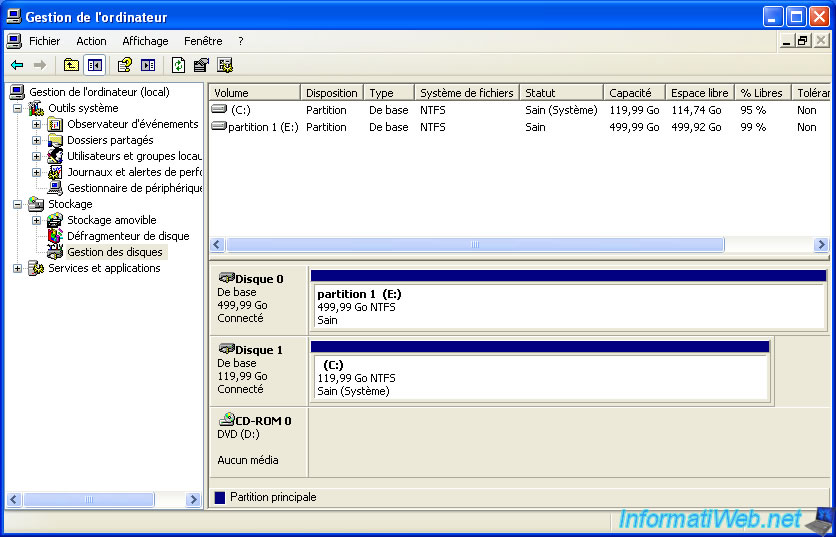
To initialize the hard drive, go to the start menu and right click on "My Computer" -> Manage.
Then, in the "Computer Management" window that appears, go to "Storage -> Disk Management" (in the left).
As you can see, your hard drive is "Not Initialized" and space is "Unallocated" (not partitioned).
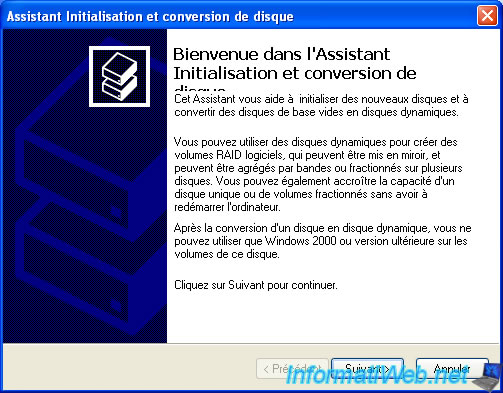
Windows XP will detect your hard disk isn't initialized and this window will appear automatically.
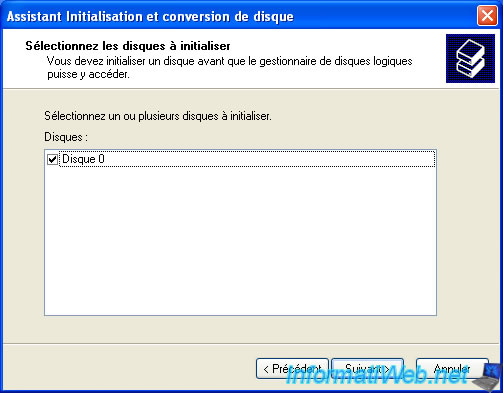
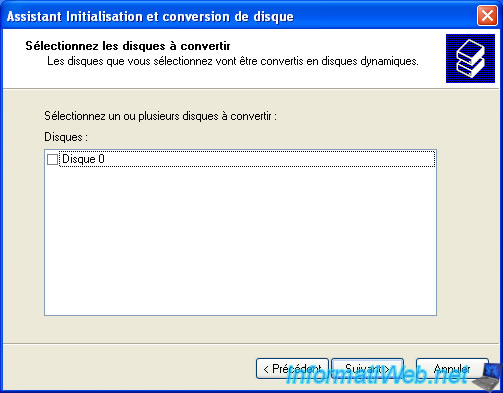
Make sure the box "Disk x" is checked.
Initialize a hard drive is to create an empty partition table.
For the conversion of the disk, make sure the box is not checked.
By default, a hard disk is "basic" but this conversion would transform it into "dynamic disk". It is possible to go from "basic" to "dynamic" easily, but the reverse is not possible (unless you delete all partitions and therefore data on the hard disk).
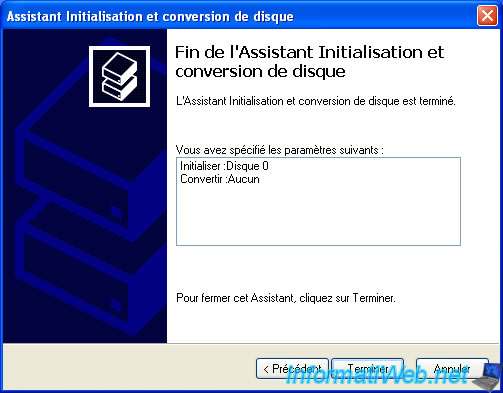
Your hard disk is initialized.
2. Create a single partition on the entire hard drive
As indicated at the beginning of this tutorial, partitioning allows to separate your data and generally separate the OS and data.
However, some people have difficulty to partition their hard drive. The easiest way is to create a single partition on the hard drive to use it. It is this type of partitioning is used for external hard drives.
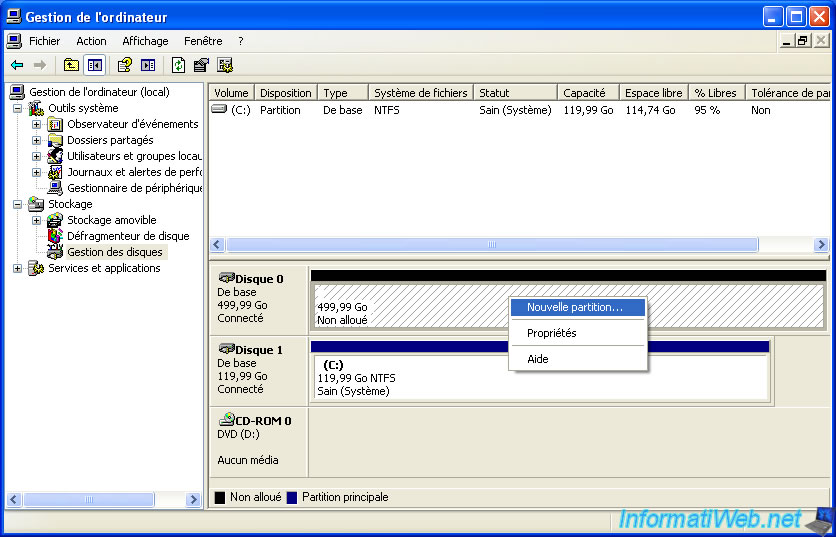
To create a single partition on a hard drive, nothing more simple. Right-click on the unallocated disk space and click "New Partition".
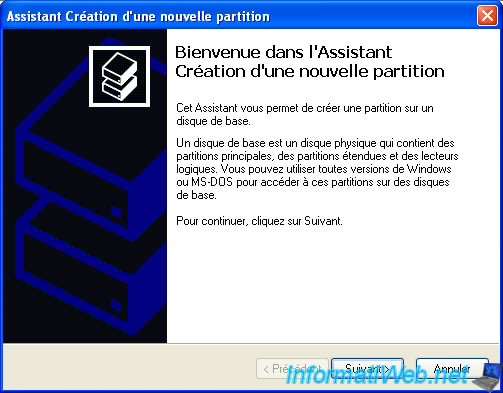
The wizard "New partition" is displayed.
Select "Primary partition".
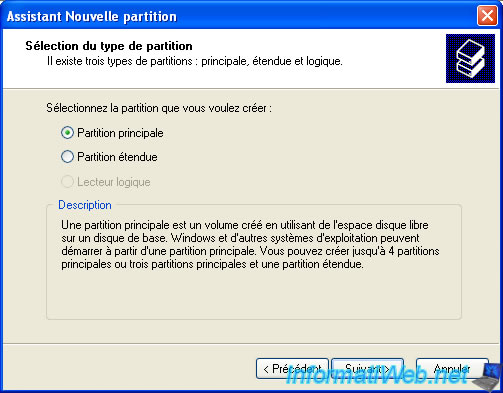
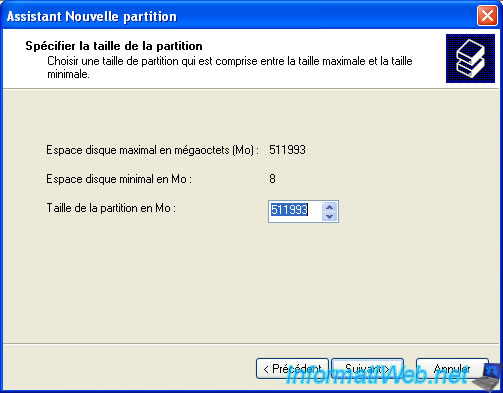
Leave the default size indicated for this partition is created on the entire disk.
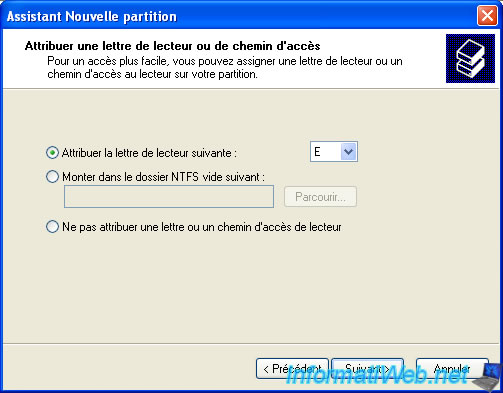
Leave the default selected letter.
Note: The wizard automatically selects the first free letter.
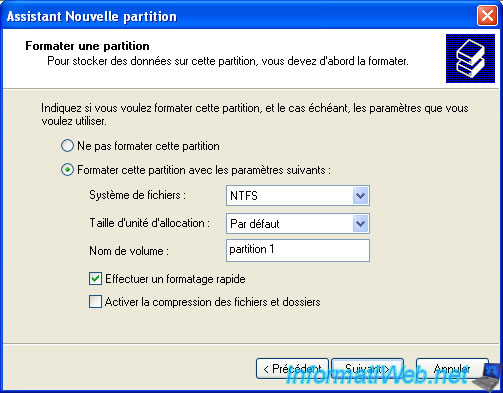
The "file system" the most used are NTFS and FAT32.
NTFS can store large files and manage NTFS permissions unlike FAT32 which does not allow it.
However, FAT32 is more compatible with different existing operating systems (Windows, Linux, Mac, ...).
The easiest way is to enter a name for your partition and check the "Quick Format" box.
Warning : Don't check the "Enable file and folder compression" box because your computer will run slower when you access files that Windows has compressed.
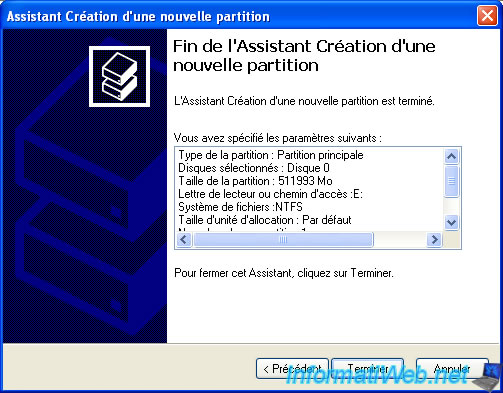
The wizard displays a summary of your settings.
Click "Finish" to create and format the partition.
The message "Formatting" is displayed for a while (depending on the performance of your computer and the size of the partition).
When formatting is complete, this message will disappear from the box and the name of your partition will be displayed.
When you go to the workstation, your partition will be displayed.
3. Create multiple partitions (for a Multiboot or normal use)
Now we will explain how to partition your hard drive correctly. That is creating primary partitions and extended partitions if needed.
Firstly, there are two types of partitions :
- The main partitions : To install an operating system partition or to store data.
- The extended partitions : that contain logical drives. These logical disks used to store data (and in rare cases, to install an OS per logical disk).
On a hard disk, you can only create 4 partitions. By against, extended partitions you can create more than 4 partitions.
More information in our article : "Why and how to partition a hard drive?".
Start by creating several primary partitions. To do this, refer to the previous point but indicate a smaller size than the default to be able to create multiple partitions.
In our case, we will create 3 primary partitions of 97.65 GB each. This will then allow us to create an extended partition that will be the 4th partition of the hard disk.

Once the 3 primary partitions are created, we will create an extended partition that contains two logical drives.
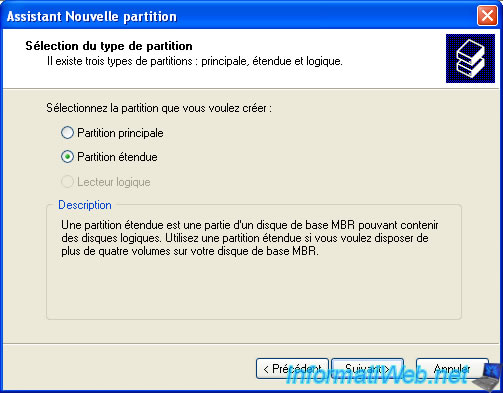
To do this, right-click on the unallocated space and click "New Partition".
Then, in the wizard, select "Extended Partition".
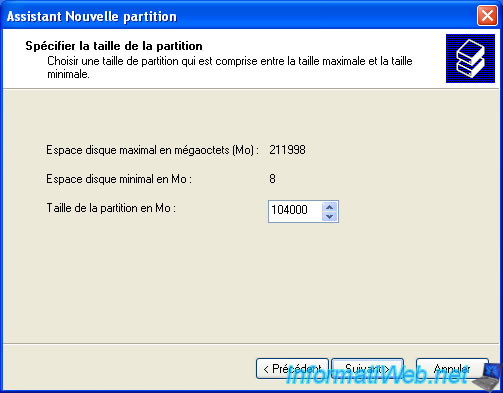
In our case, we will leave the size indicate for this extended partition takes up all the remaining (unallocated space) on the hard drive.
The wizard does not ask you for the name or the file system because an extended partition is a virtual block that contain logical drives (comparable to partitions but are not recommended for the creation of a Multiboot because it complicates things).
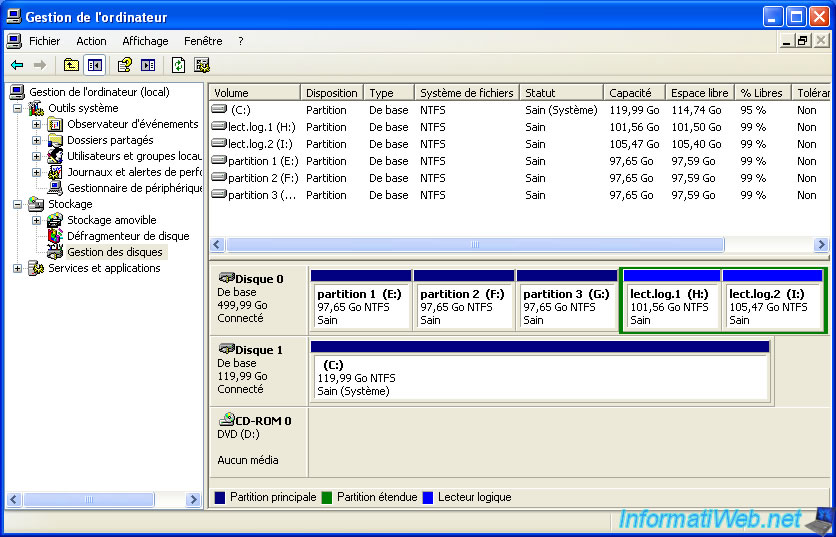
As you can see in the "Disk Management" window, the extended partition that we just created is surrounded by green and it says "Free Space". Indeed, this virtual partition contains no partition.
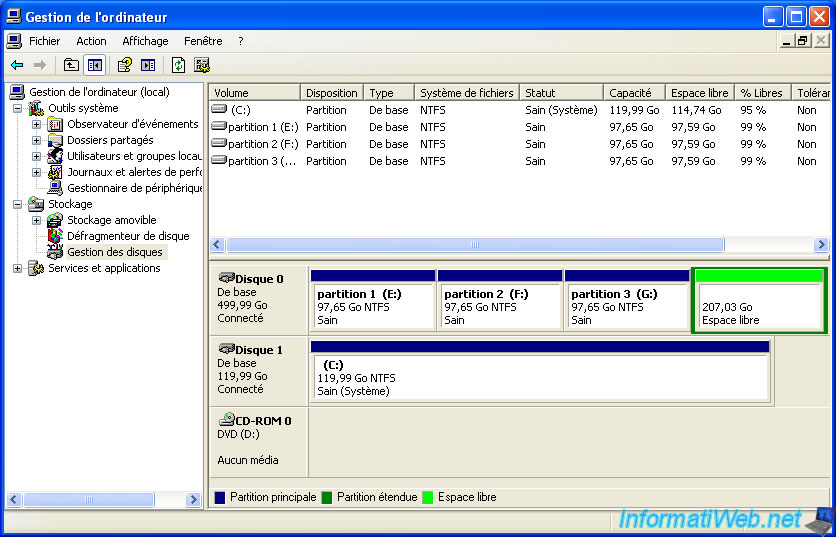
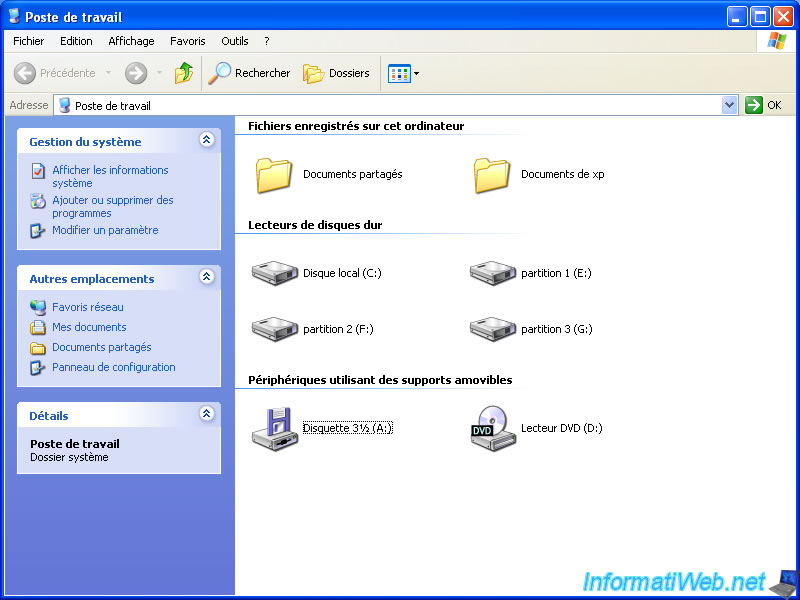
Besides, if you go to the desktop (or computer), the extended partition does not appear.
Note : 3 partitions displayed correspond to three primary partitions we just created.
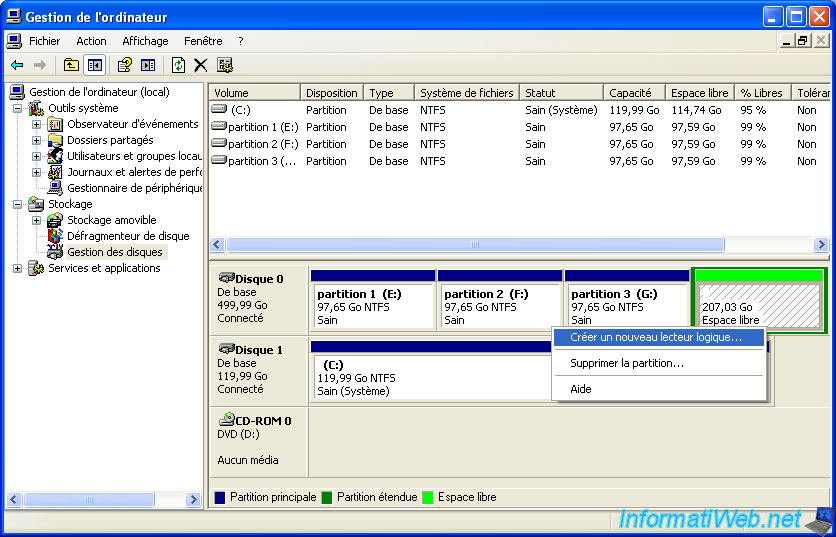
To use your extended partition, you must create logical drives. To do this, right-click on the extended partition (in free space) and click "Create a new logical drive".
Specify a smaller size than the default if you want to create multiple logical drives in the extended partition.
In our case, we will create two logical drives.

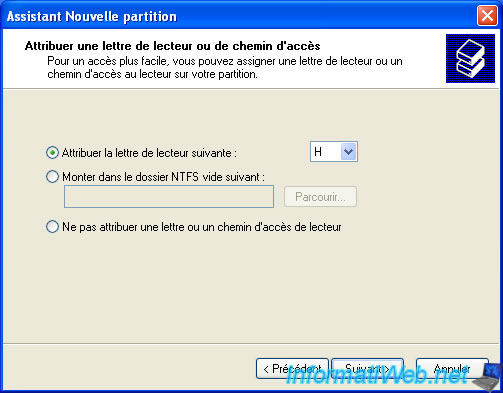
Change the letter if you wish.
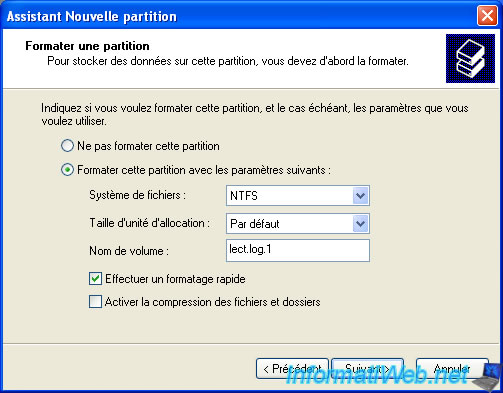
Change the file system if necessary, specify a name for the logical drive and select "Perform a quick format" for the formatting takes less time.
Caution : Don't check the "Enable file and folder compression" because your computer will run slower when you access your files.
Now we have 3 primary partitions + 2 logical drives (which are comparable to partitions).
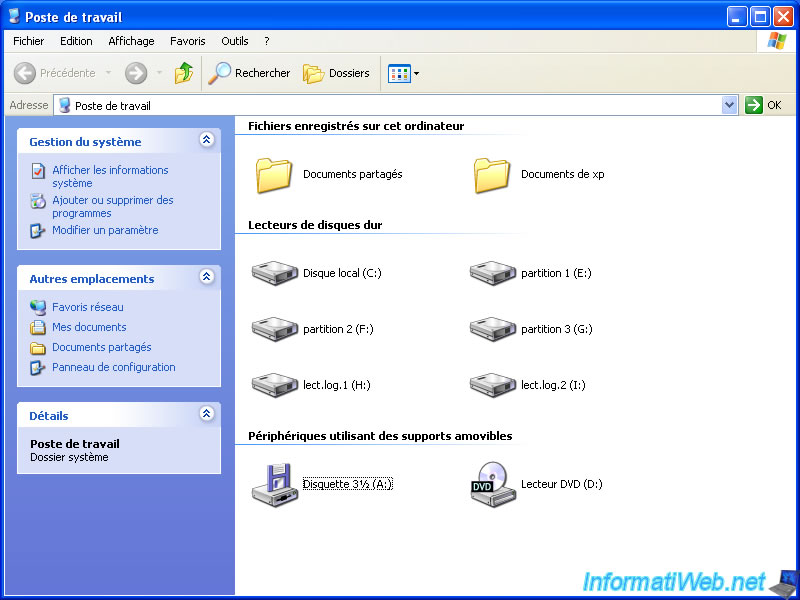
If you go to the desktop (or computer), you will see that the primary partitions and logical drives are displayed in the same way.
To store your data, this system is no problem of compatibility. By against, if you decide to create a multi-boot, you will see that the use of primary partitions is recommended.
Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Windows 11/3/2013
Windows XP - Connect to a Wifi network
-

Windows 11/22/2012
Windows XP - Create a bootable USB key to install Windows
-

Windows 12/25/2012
Windows XP - Install Windows XP on a SATA hard disk
-

Windows 3/14/2013
Windows XP - Repair installation of Windows

You must be logged in to post a comment