- Articles
- USB keys
- 02 November 2014 at 16:32 UTC
-

As USB storage devices, you have :
- USB key (well known), with a maximum capacity of 64 GB (for now)
- External hard drives (which are actually hard drives SATA or IDE, we can plug into an USB port via a standard hard disk controller and an USB cable that comes out of the case)
- Memory cards (SD, μSD, Memory Stick ...) readable with a card reader that supports the desired type of card.
- Smartphones : In general, it's possible to access files of their smartphone by connecting it using the USB cable supplied with the unit.
- Unplug an USB drive safely
- Store files larger than 4GB
- Prevent the spread of viruses via USB supports
- Hard drives are fragile
- Hard drive or SSD ?
- Defragmenting an USB support, it's a good idea ?
1. Unplug an USB drive safely
Generally, people know that USB drives are automatically recognized (thanks to Plug and Play) when you plug the USB key on a computer.
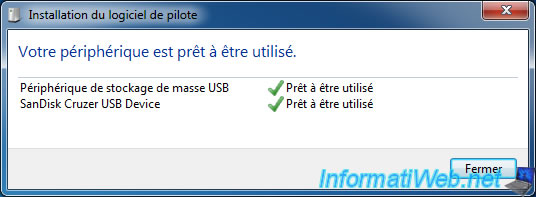
However, few are the people know that USB keys must be ejected (removed from memory) before being disconnected. Indeed, most of the time, people unplug their USB drives when not in use more. While this may seem normal, know that this habit is one of the causes of problems with your USB keys (USB keys that no longer work, loss of data, which requires Windows to format it, ...).
To properly unplug an USB drive (or any other type of USB storage device), you just have to use the icon ![]() and click "Eject [Name of your USB drive or USB storage device]".
and click "Eject [Name of your USB drive or USB storage device]".
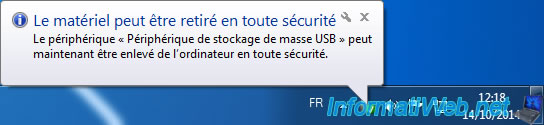
After a few seconds the message "Safe to remove hardware" will appear.
2. Store files larger than 4GB
By default, USB keys are formatted in FAT (or FAT32).
This file system is most compatible between different operating systems but has a limit. Indeed, the FAT32 file system is limited in several ways :
- The maximum size of each file : 4GB
- Maximum number of files : over 250 million
- Maximum size of the file name : 255 characters (UTF-16)
- Etc.
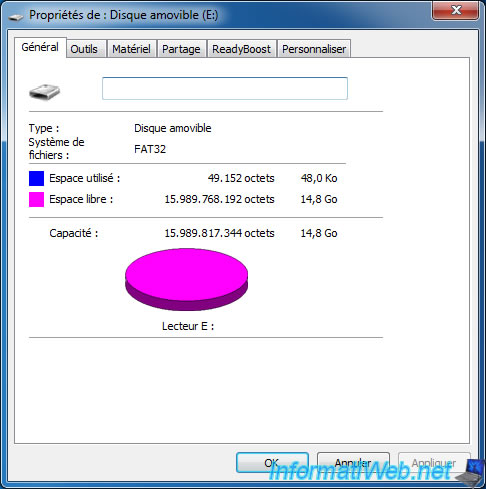
If you try to store a file of more than 4 GB on an USB drive in FAT32, Windows will display the message "The file [filename] is too large for the destination file system".
Unnecessary to make space on your USB drive because the limitation is located at the FAT32 file system and not in free space (as you can see on the picture below).
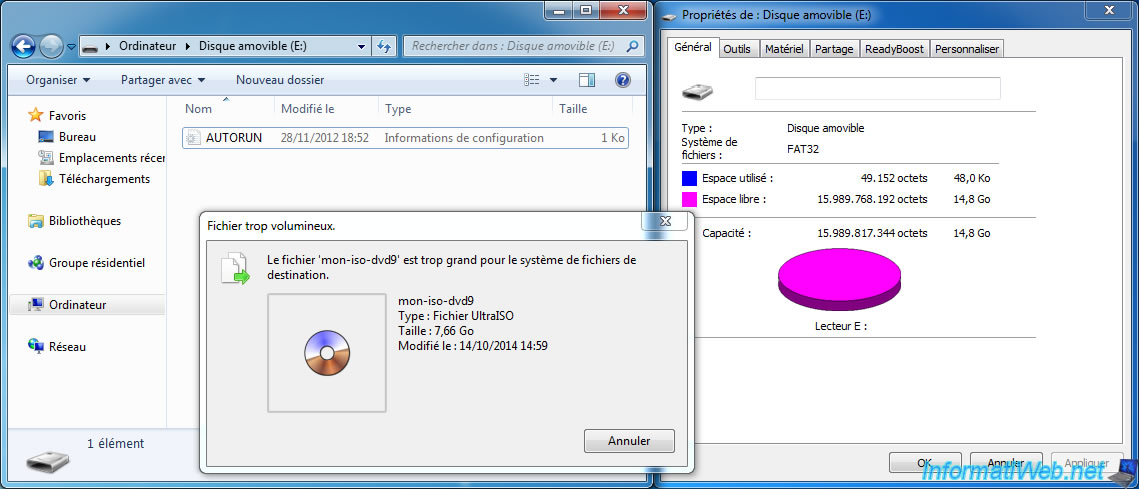
To store or transfer files of more than 4GB, you have 2 options :
- Use the NTFS file system
- Split your files using 7-Zip, WinZip or WinRAR
2.1. Use the NTFS file system
To change the system from your USB drive, nothing more simple. Just format your USB drive to NTFS.
Caution : Formatting erases all data on the USB drive.
To format your USB drive in NTFS, go to the desktop (or Computer) and right click on your USB drive (or removable disk) . Then, click on "Format".
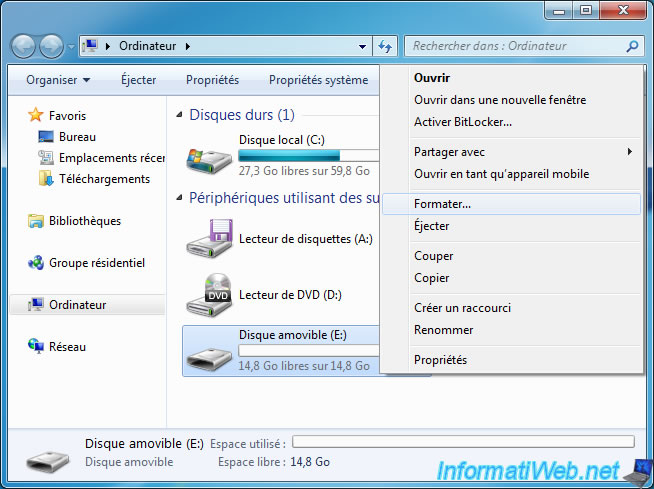
The "Format Removable Disk X" opens.
Select "File system : NTFS".
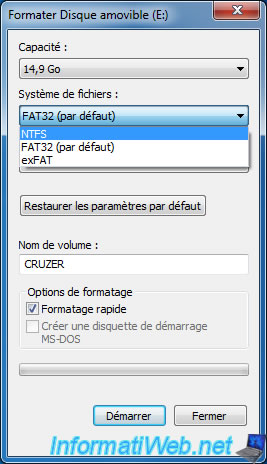
Warning : Formatting erases all data on the USB drive.
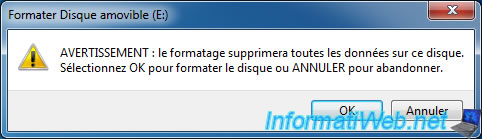
Once it's done, our 7.66 GB file can be copied to our USB drive in NTFS.
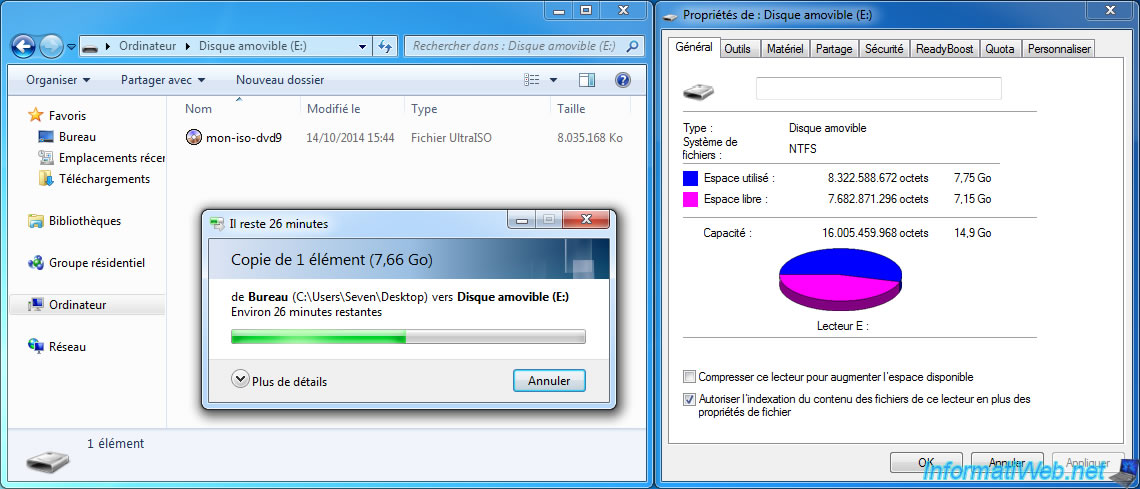
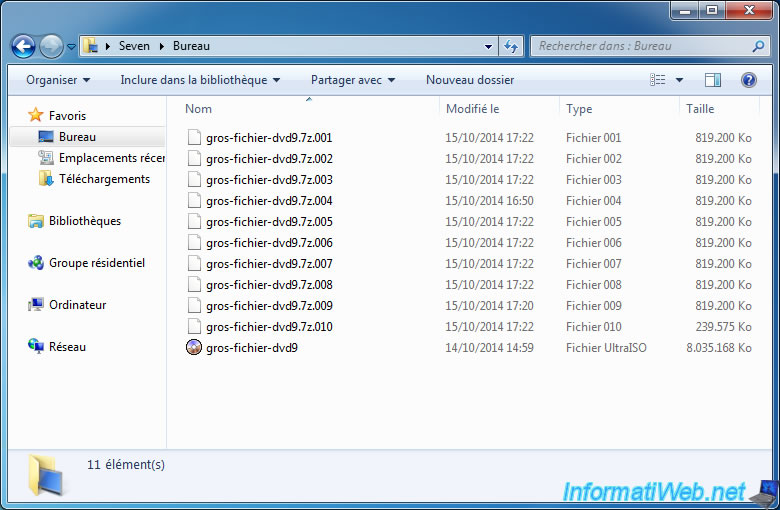
2.2. Cut your files using 7-Zip, WinZip or WinRAR
This second solution has advantages and disadvantages :
- The major advantage : compatibility of the file system (FAT default for USB drives)
- Disadvantage : You can't use your original file directly from your USB drive. You will need to unzip the files list to get your original file.
To split a file into multiple files, you can use a compression software like : 7-Zip (free), WinRAR (fee but known) or WinZip (fee but known).
To do this, refer to our tutorial : "Cut large files with 7-Zip or WinRAR".
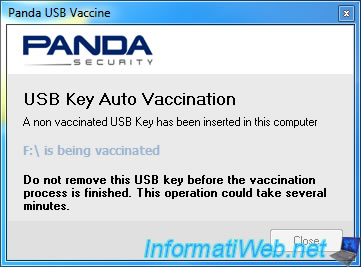
3. Prevent the spread of viruses via USB supports
Today, USB keys are increasingly used to carry information or transfer them from one computer to another. And of course, hackers know it; So they use the famous "autorun.inf" file to spread their viruses on different computers you access. The "autorun.inf" file was designed, basically, to help the user by allowing the automatic launch of the desired file on the CD / DVD inserted the computer. However, this file also works with USB sticks.
To prevent the spread of viruses via USB supports, we must prevent hackers from using the "autorun.inf" file.
To do this, refer to our tutorial : "Prevent the spread of viruses by USB media".
4. Hard drives are fragile
First, there are two kinds of hard drives :
- Internal hard drives (2.5" and 3.5")
- External hard drives (2.5" and 3.5")


First, all hard drives are fragile. They are much more reliable than before, but their data capacity increase. This means that a 2.5" hard drive will be more fragile than the equivalent in 3.5".
4.1. Internal hard drives
So, what to choose as internal hard drive ? 2.5" or 3.5" ?
In fact, it depends on its use :
- For laptops : only 2.5" are possible
- For desktop PCs : the standard size is 3.5" but you can use a 2.5" (for a : Adapter for HDD / SSD 2.5" in a bay 3.5") recovered from a laptop or any other computer if you wish.
The problem with hard drives is that there is a physical movement inside (read heads that float about ten microns above and below the hard disk platters). And when the hard drive receives a shock (in functioning), it has a big chance to create bad sectors on the hard drive. Obviously, the impact is less severe on a 3.5 "hard drive, than on a 2.5" hard drive, because the disk is much greater in the 3.5" .

If a hard drive (not in functioning) falls a few inches, it will not cause any problems. However, in functioning, there will be some damage.
If we specify this, it's for you to understand that you should never move a laptop running. It's portable, but not in running state (unless you replace the hard drive by a SSD).
4.2. External Hard Drives

So, what to choose as external hard drive ? 2.5" or 3.5" ?
3.5" without hesitation. It's true that the 3.5" hard drives take a bit more space than 2.5" hard drives, but your data will be safer in a 3.5" HDD rather that a 2.5". Why ? for the same reasons that internal hard drives. The data blocks are larger on a 3.5" hard drive than on a 2.5" hard drive. If the external hard drive receives a shock, 2.5" would be more damaged than the 3.5" hard drive.
Now, if you need to transport a lot of information with you, the 3.5" hard drive will not fit in your pocket (unless you have a big solid pocket). Besides, we don't recommend it because all shocks received by the hard drive may cause problems, over time.
The only reliable solution is to use a SSD (which are all in 2.5" format). They are much less sensitive to shocks (unless you letting it fall very high).
For what reasons ? To that described in the next section of this article.
5. Hard drive or SSD ?

The main differences between hard drives and SSDs can be found at :
- Speed ​​: A SSD is much faster than a hard drive because there is no mechanical movement in the SSD.
- Functioning :
The hard drive is composed of plates with read heads moving to read the data.
While the SSD is simply composed of memory chips. So there is no physical movement in the SSD.
- Fragility :
When a hard drive receives a shock, the read heads clap on discs located inside. This can cause bad sectors on the hard disk.
SSD isn't sensitive to shock (unless you drop it of high)
- Transport :
Keep a hard drive in your pocket is risky for the reason mentioned above.
Keep a SSD in your pocket doesn't damage it (unless he gets a bad shot. Example : with the corner of a table).
- Price :
The hard disk is cheap because it's common.
SSD is expensive per GB but has good benefits (including speed and security when transporting data)
For information : a SSD can be compared to a large USB key.
6. Defragmenting an USB support, it's a good idea ?
Defragmentation itself is a good idea because it improves the performance of your computer.
Without enters too much in theory, know that a file is stored in a series of blocks (or cluster in English). When this file is stored in blocks side by side, the read head can quickly read the entire file. Conversely, when the file is "fragmented", the file is located in blocks scattered on the hard drive. In this case, the read head takes longer to read the file because it must cover a greater portion of the disk to read the entire file.
Defragmentation is a good idea because it "glue together" (in other words) the different pieces of the file to put them side by side.
Defragmentation is generally recommended. Except that this is true only for hard drives (whether internal or external).
For USB keys, memory cards or SSD , you should never defragment them. It serves no purpose for these data supports and would unnecessarily reduce their lifespan.
Indeed, a SSD fragments itself (without altering their performance) to extend their lifespan. In fact, memory chips of SSDs have a limited number of reads and writes. To avoid using all the time the same cells, the SSD moves different parts of the file in other cells. If you defragment an SSD every day, the cells used will always be the same and you will decrease the life of your SSD unnecessarily. Besides, you go against its normal operation and the SSD will continue to fragment itself voluntarily.
Now that you know more about defragmentation, know that on Windows (Vista, 7, 8 and higher), defragmentation is enabled by default for all hard disks and disabled for SSD.
Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Articles 2/17/2017
Corsair Flash Padlock 3 - Secure USB key with hardware encryption
-

Articles 2/8/2017
Kingston DataTraveler Locker+ G3 - Secure USB key
-

Articles 1/21/2017
Presentation of the various USB keys
-

Windows 2/27/2017
WTG - Windows workspace on USB key

You must be logged in to post a comment