- Windows
- Windows 8 / 8.1, Windows 10, Windows 11
- 03 April 2025 at 07:57 UTC
-

Since Windows 8, you can create "Parity" type storage spaces (which corresponds to a software RAID 5 if you use 3 physical disks).
This allows you to create more efficient storage and protect against the failure of a physical disk.
If your storage space is almost full and you are running out of space for your new data, you can easily expand it by adding one or more additional physical disks.
Tutorial made on Windows 10 version 2104 and also tested with Windows 11 v21H2, 8.1 Pro and 8 Pro.
- Create a parity storage space (RAID 5)
- Add a physical disk to expand your storage pool
- Increase the size of a parity storage space (RAID 5)
- Unchanged fault tolerance with 4 physical disks
1. Create a parity storage space (RAID 5)
On Windows, to create a "Parity" type storage space (software RAID 5), you just need to select the "Parity" resilience type.
As Windows tells you, on a storage space with parity, Windows writes your data with parity information.
More precisely, in the case of this "Parity" type storage space, Windows will write:
- half of each data on the 1st physical disk.
- the other half of each data on the 2nd physical disk.
- parity data on the 3rd physical disk.
In case of a physical disk failure, Windows will be able to recalculate the missing disk.
Since Windows must also write parity information, it is normal that the default value (which will be the size of your storage space) is less than the available pool capacity and the "Including resiliency" value.
The "Including resiliency" value includes the disk space available for your data, as well as the disk space required for the parity information.
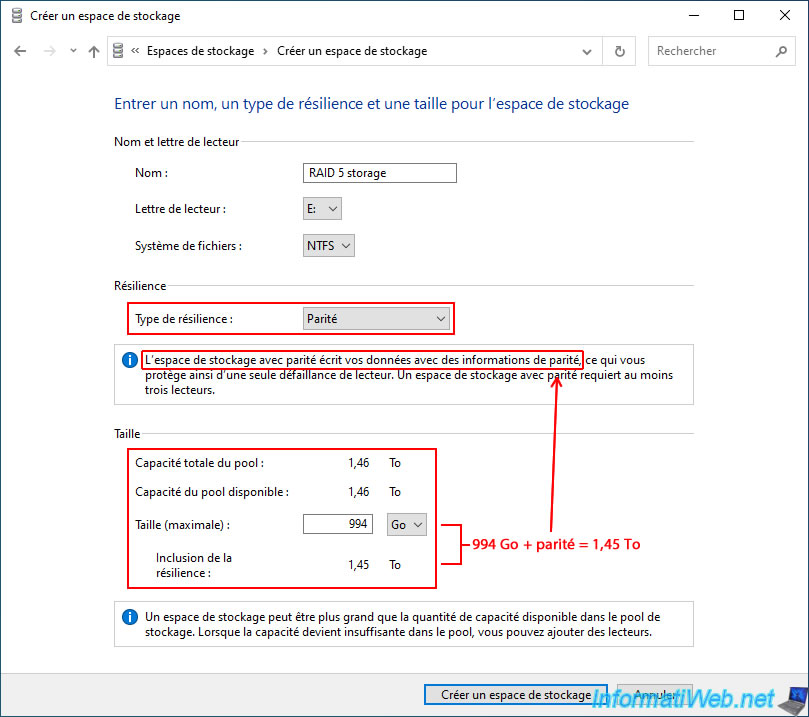
As you can see, the size of your storage space (already visible previously) is necessarily less than the total size of your storage pool (due to the disk space reserved for parity).
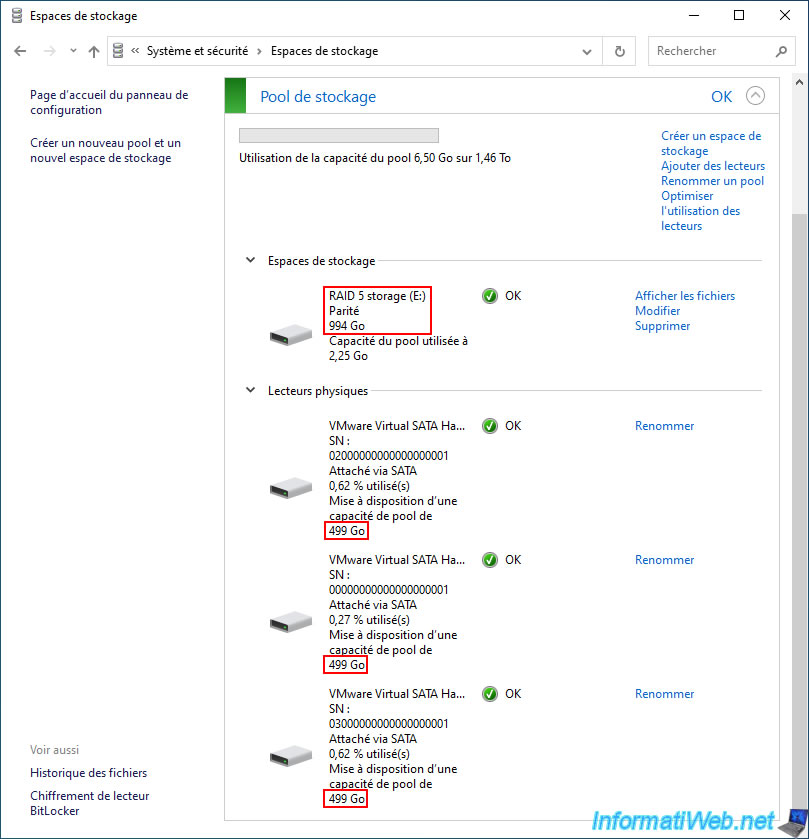
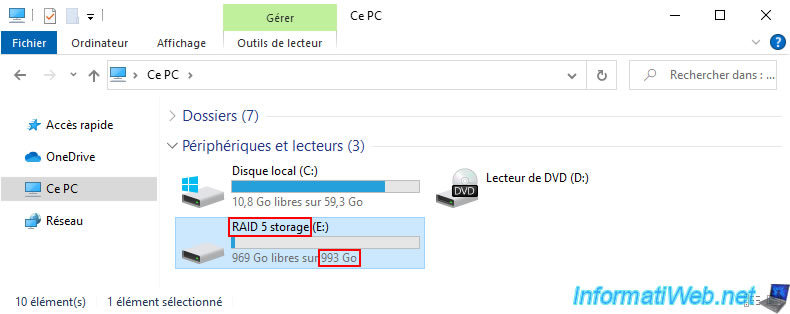
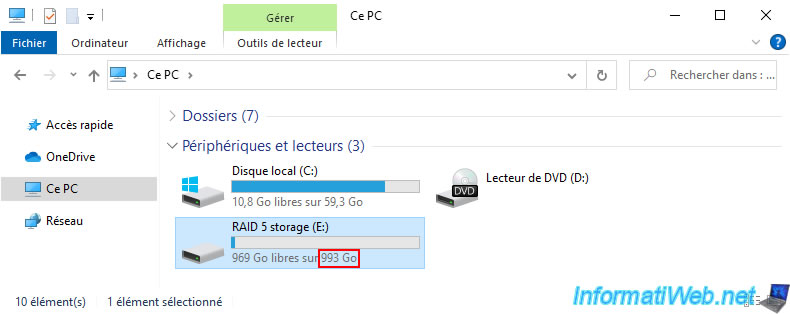
In file explorer we can see that our "RAID 5 storage" storage space is currently 993GB (about 1TB) in size.
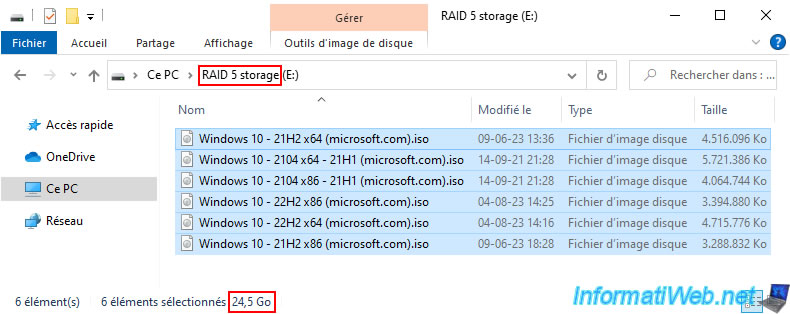
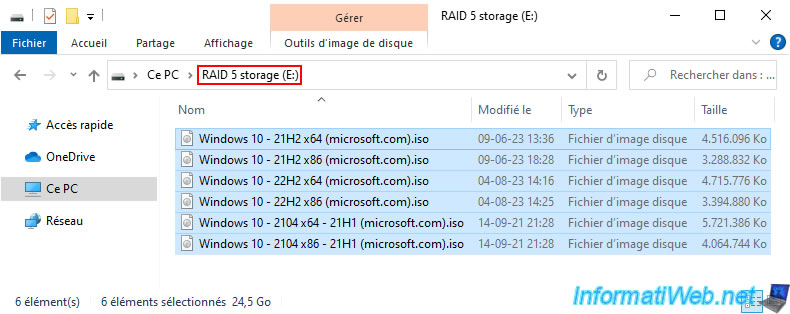
We added several gigabytes of data to this storage for testing.
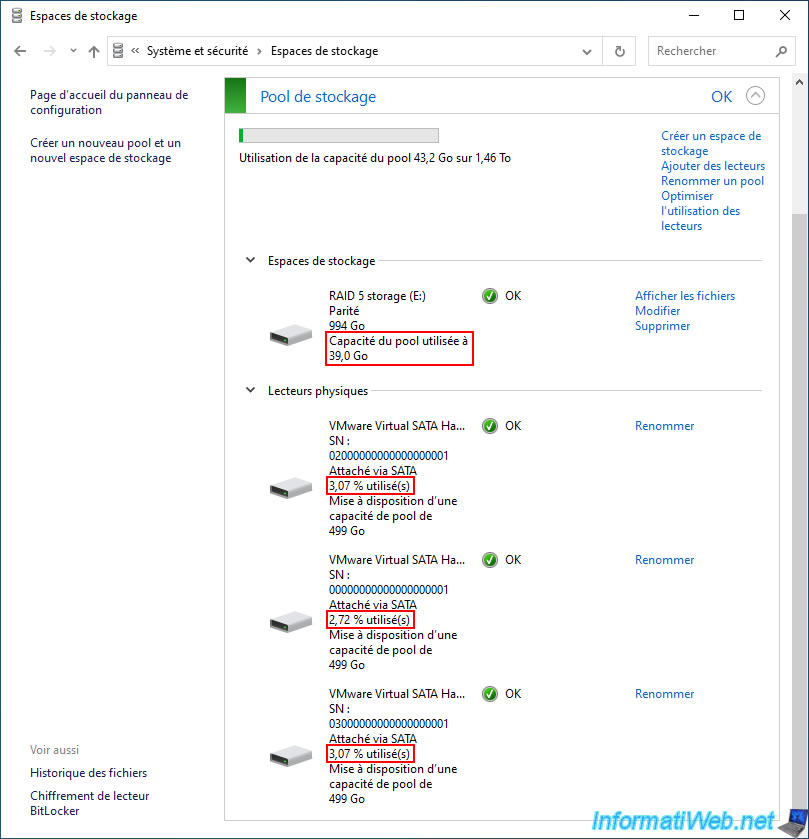
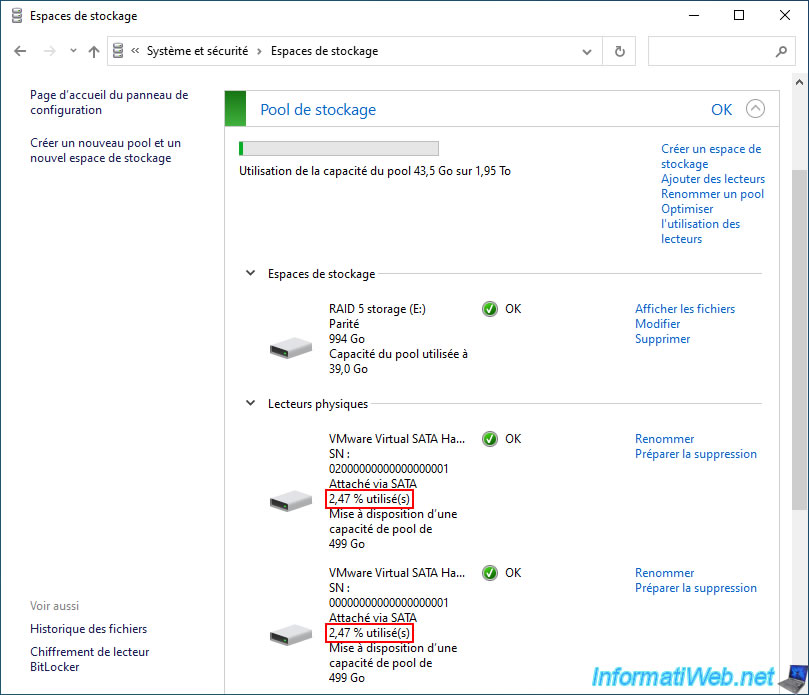
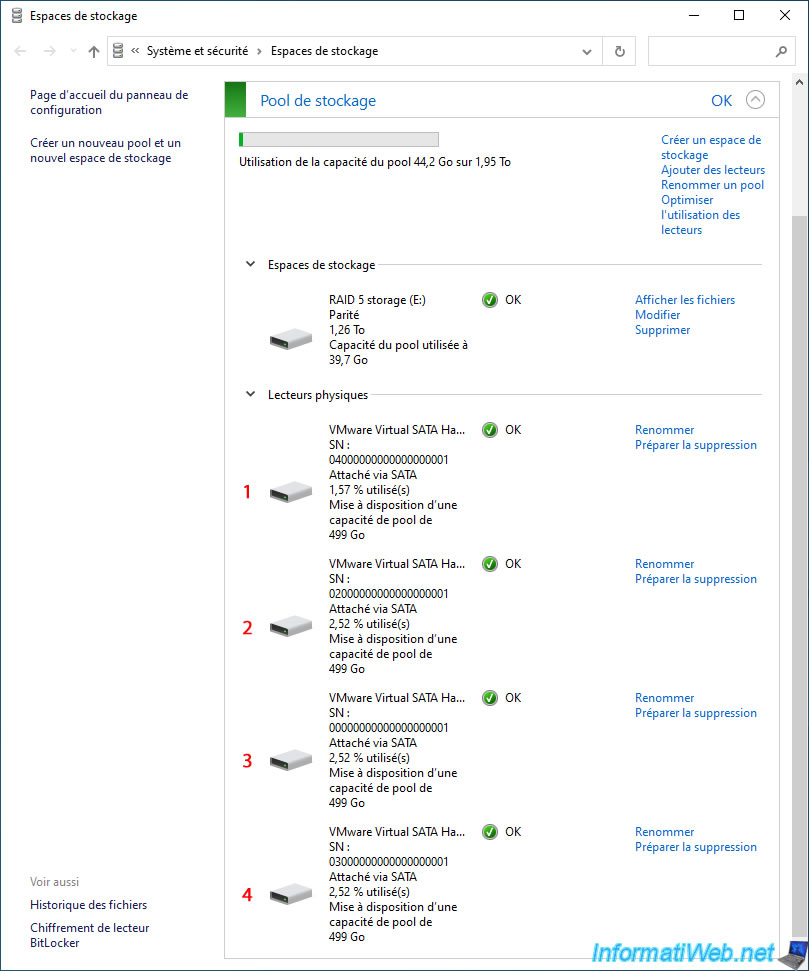
As expected, the usage percentage of your physical disks has changed and is the same on 2 disks (the ones containing the stored data).
The 3rd disk contains parity data. This allows later to recalculate the physical disk that would have failed.
For the pool capacity usage, you can see that we have used 39 GB while the stored data takes 24.5 GB.
Again, this is due to the parity data that was written automatically by Windows (although you don't see it).
2. Add a physical disk to expand your storage pool
Later, if you need more disk space on your "Parity" storage space, you will need to plug an additional physical disk into your computer (by turning it off first, of course).
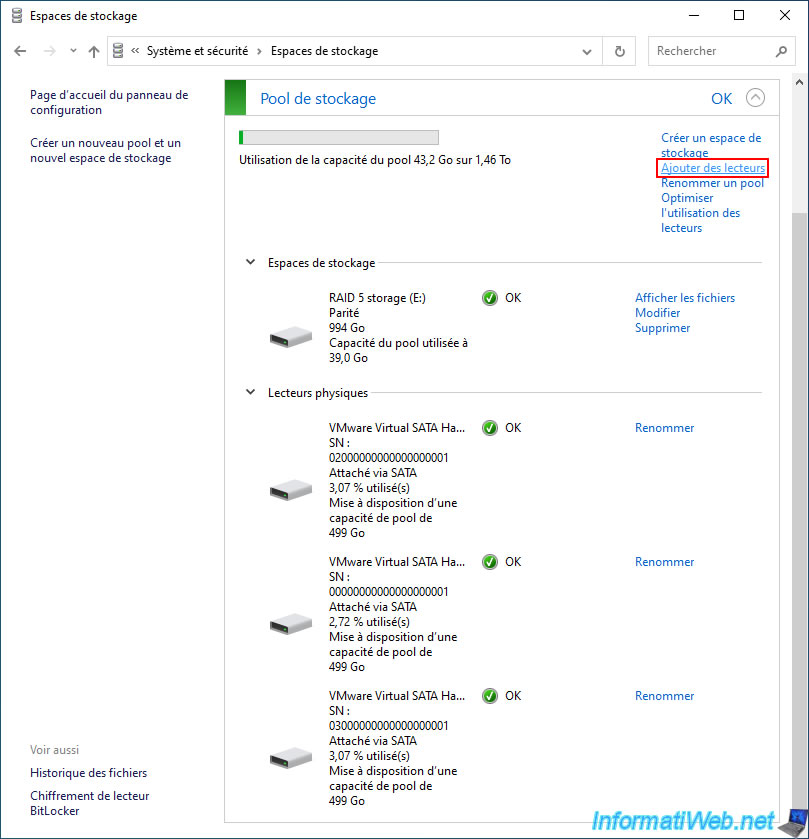
Then, go back to the "System and Security -> Storage Spaces" section of the control panel and click on the "Change settings" button (located at the top of the window).
Then, click on the "Add drives" link (boxed in red on the image below).
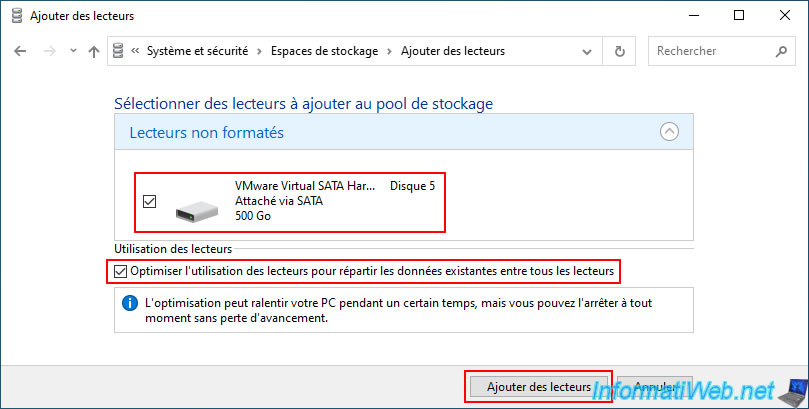
Select the new physical disk that you have just plugged into your computer and preferably check the box "Optimize drive usage ..." so that Windows distributes the current data of your storage space on the different physical disks of your storage pool.
Then, click on the "Add drives" button to validate.
Note: the "Optimize drive usage ..." option is optional and only available since Windows 10.
If you have checked the box "Optimize drive usage...", the message "Optimizing drive usage..." will appear.
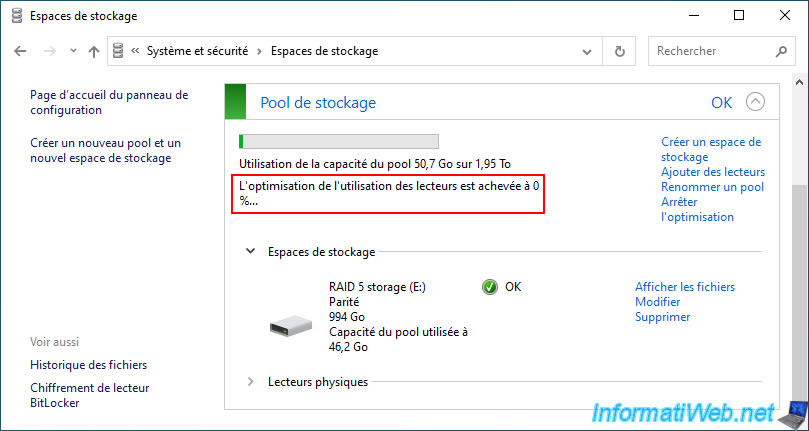
As you can see, a new physical disk has appeared at the end of the "Physical drives" list.
Also, you will see that the usage percentage of the new physical disk will gradually increase as the drive usage is optimized.
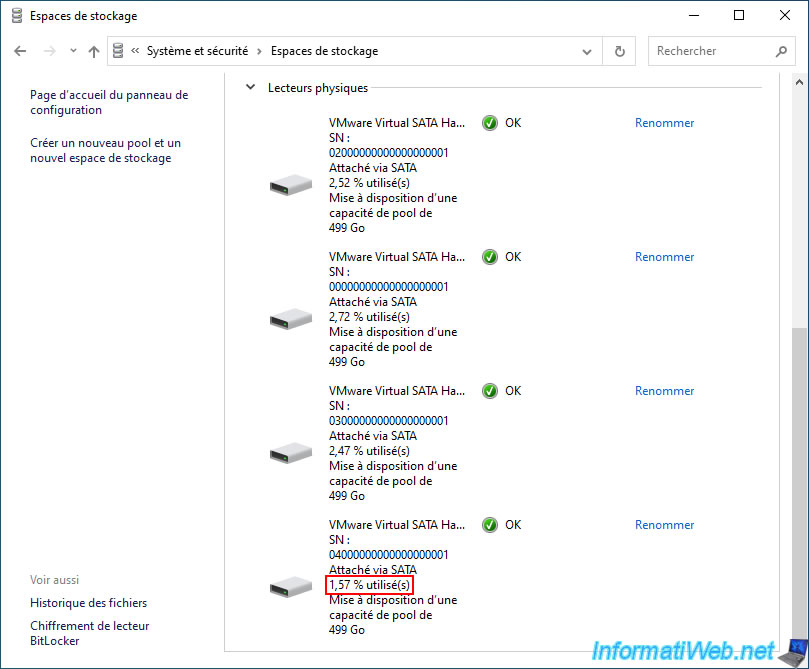
Once the drive usage optimization is complete, the "Optimizing drive usage..." message will disappear and you will be able to see that the usage percentage will be almost the same across the physical disks (physical drives) in your storage pool.
However, despite adding the physical disk to your storage pool, you will notice that the size of your "RAID 5 storage" storage space has not changed in file explorer.
3. Increase the size of a parity storage space (RAID 5)
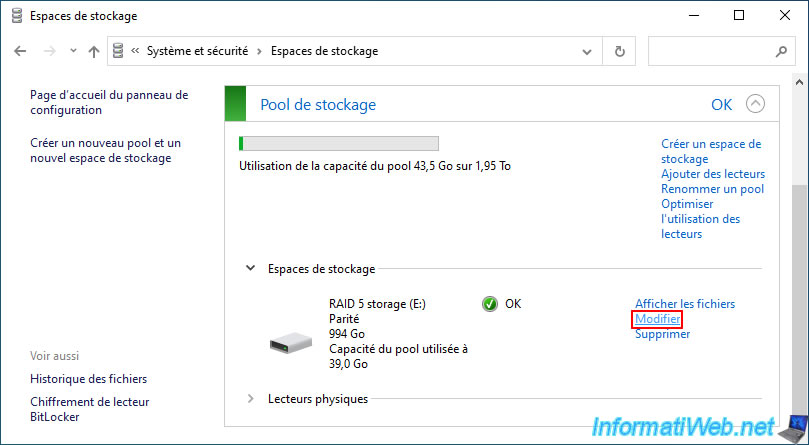
To be able to use the space available on your new physical disk, you must modify the size of your storage space.
To do this, click on the "Edit" link located to the right of your "Parity" type storage space.
By default, Windows will indicate the current size of your "RAID 5 storage" storage space in the "Parity" box.
In our case: 994 GB.
As you can see at the bottom of the window, it's technically possible to create a storage space that is larger than the capacity (size) of your storage pool.
If you do this, and then try to store too much data in your storage space, Windows will eventually ask you to add a physical disk when the actual available space is no longer sufficient.
However, we will not do this here.
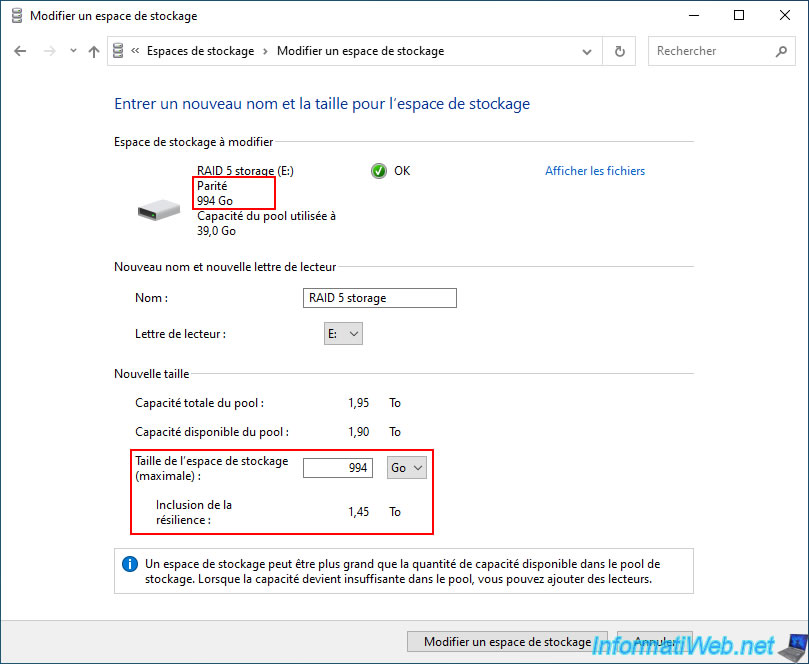
To use only the space that is actually available on your storage pool (also counting the disk space reserved for parity), you need to know the ratio between the "Storage space size (maximum)" value and the "Including resiliency" value.
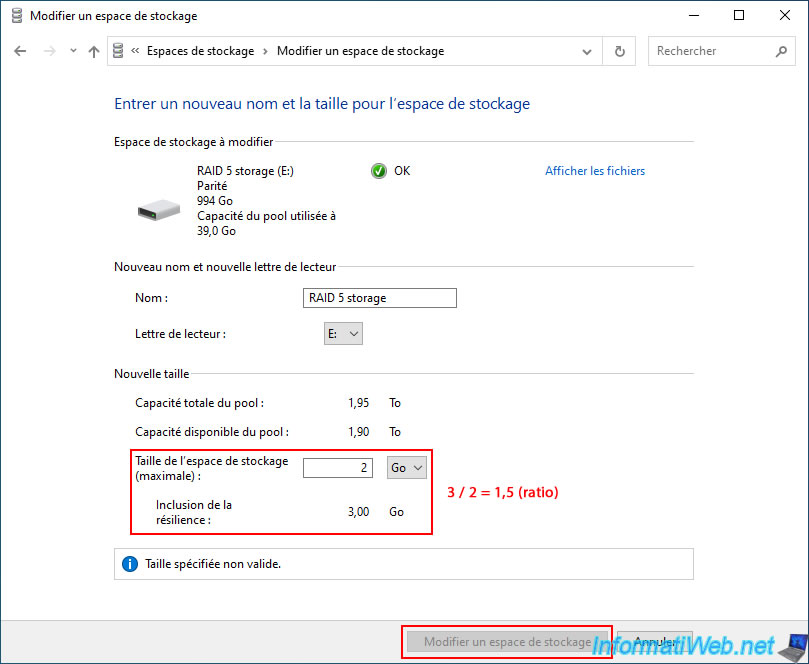
To do this, we recommend temporarily indicating the value "2" (GB) in the "Storage space size (maximum)" box.
Then, divide the "Including resiliency" value (3) by the "Storage space size (maximum)" value (2).
Normally, with a "Parity" type storage space, you will get a ratio of 1.5.
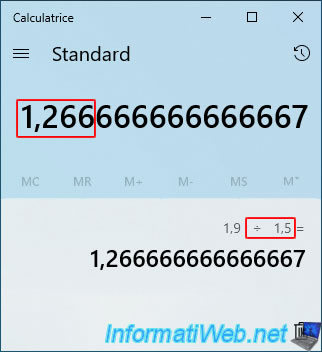
Now, divide the "Available pool capacity" value (in our case: 1.9 (TB)) by the ratio found previously (normally: 1.5) and you will get the value to indicate in the "Storage space size (maximum)" box.
So, in our case: 1.266 TB.
Enter the value obtained (keeping only 3 decimals) in the "Storage space size (maximum)" box.
Note: don't forget to change the storage unit (e.g.: TB, GB, ...) if necessary.
In our case, we can therefore use 1.266 TB of disk space (with 4 physical disks of 500 GB) instead of 994 GB (with 3 physical disks) as was the case previously.
Once the size has been modified, click on the "Modify storage space" button.
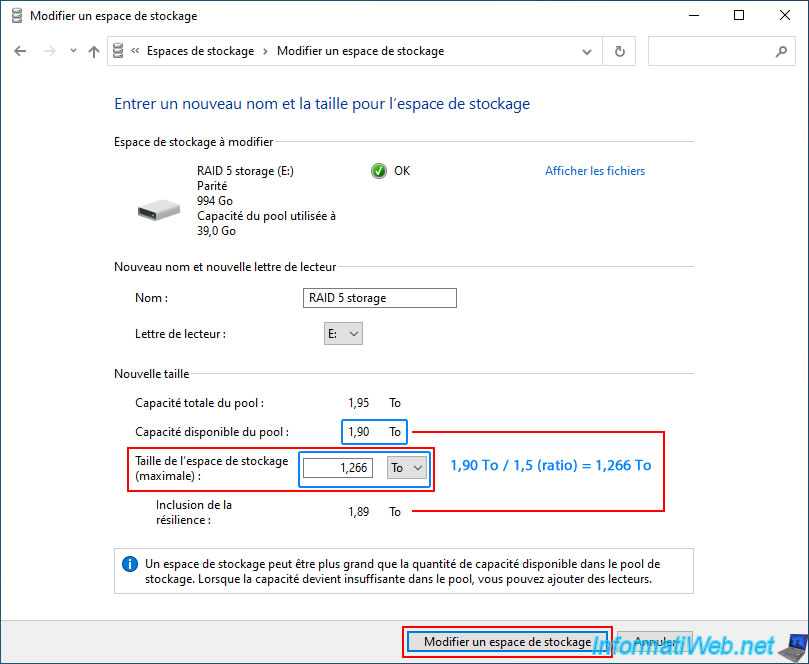
As expected, the size of your "RAID 5 storage" storage space has been successfully modified in the "Storage spaces" section of the control panel.
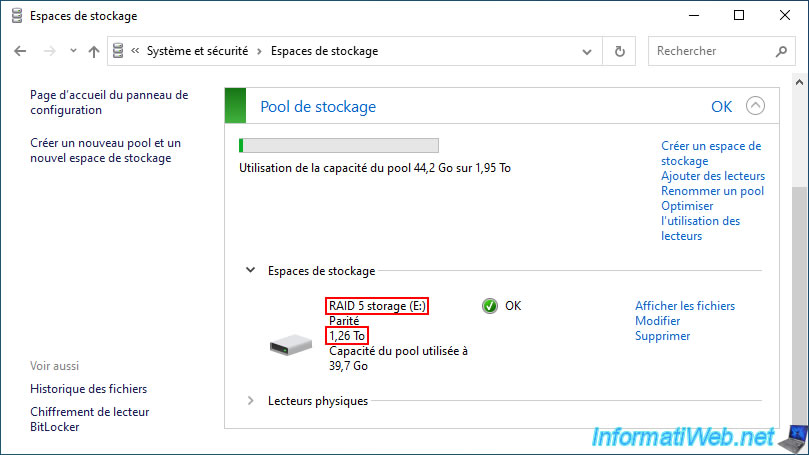
In file explorer, you will also see that your storage size has increased.
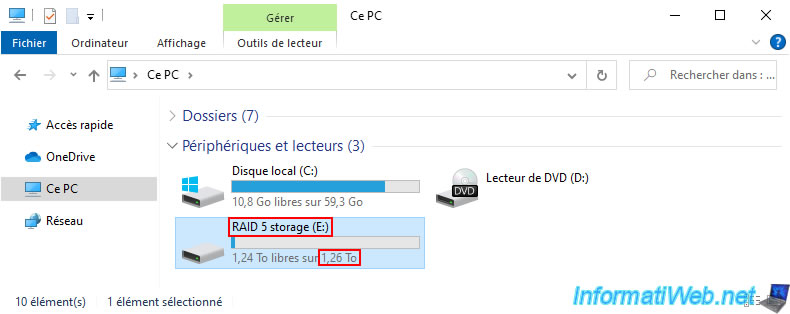
If you open this one, you will obviously see that the data is still there.
4. Unchanged fault tolerance with 4 physical disks
By default, a "Parity" storage space requires at least 3 physical disks and is protected against the failure of a single physical disk (no matter which one fails).
Note that adding a 4th one will not change the current fault tolerance.
If a physical disk fails, your storage space, as well as its corresponding storage pool, will be in warning.
This means that all data in your storage space is still available and you should replace the failed disk as soon as possible before a 2nd physical disk fails.
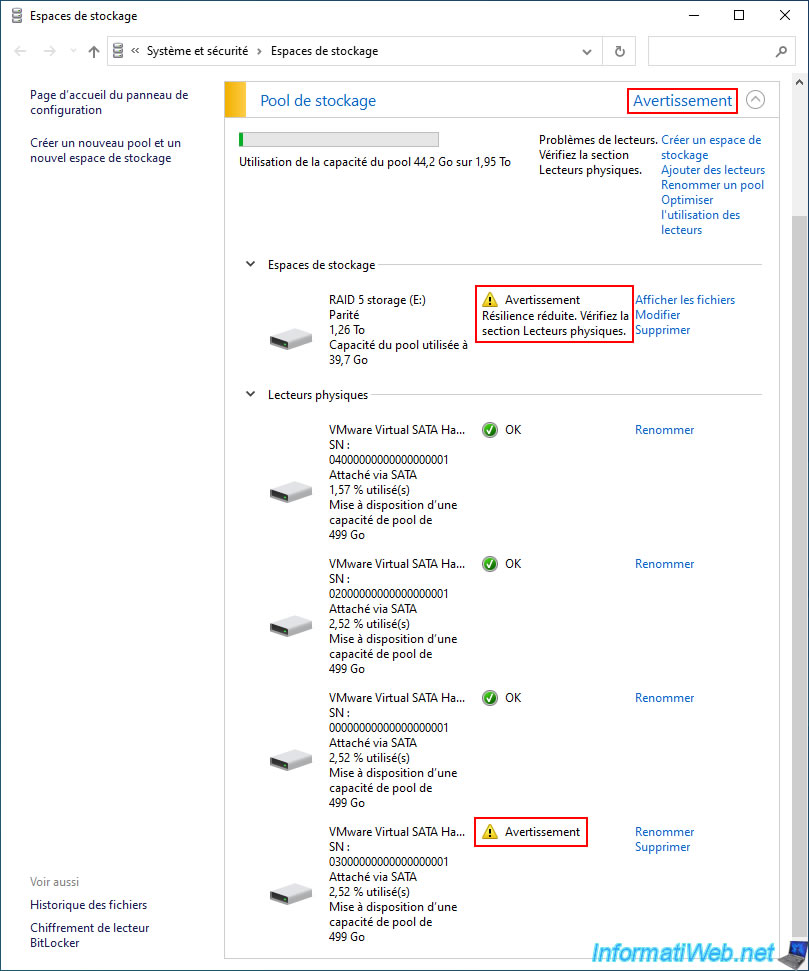
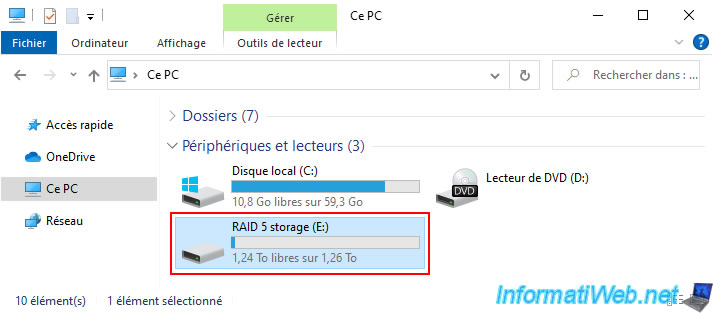
By the way, if you go to the file explorer, you will see that your "RAID 5 storage" storage space still appears there.
Moreover, you can use this data without any problem despite the failure of a physical disk.
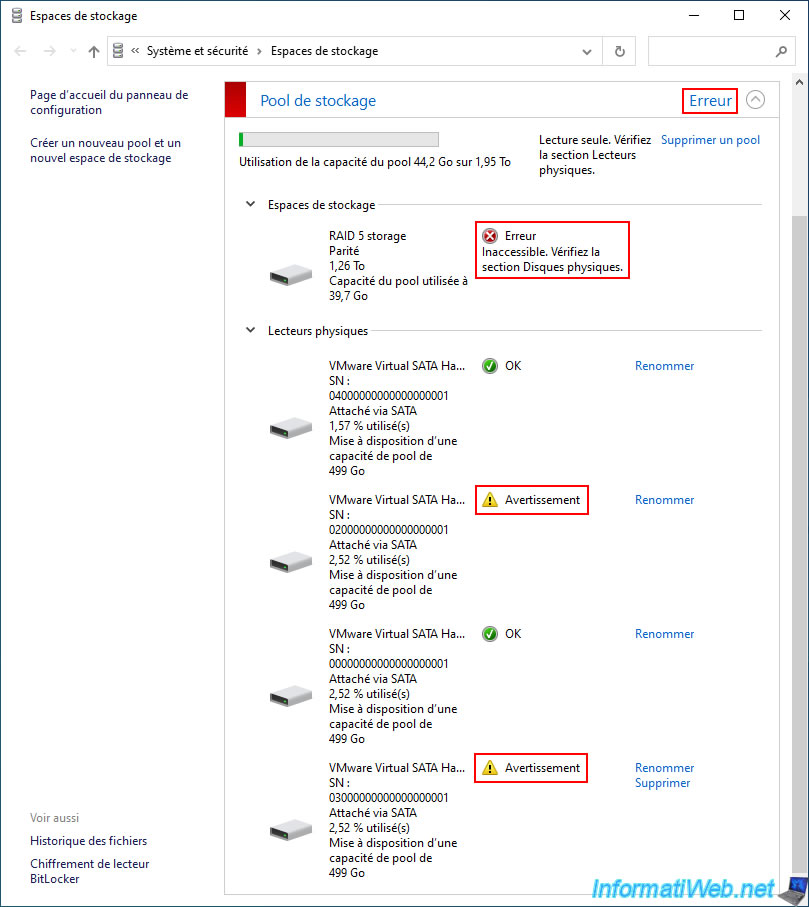
On the other hand, if a second physical disk fails, your "Parity" type storage space and your storage pool will be in "Error" status.
The fault tolerance therefore remains at 1 physical disk maximum.
Important : although the Microsoft site indicates that the fault tolerance increases to 2 failed physical disks from 7 physical disks with "Parity" type storage, this is false (including on Windows 10 and Windows 11).
In reality, the fault tolerance will remain at 1 failed physical disk, even with 7 physical disks.
If 2 or more physical disks fail for your "Parity" type storage, Windows will show you this notification.
Plain Text
Check for storage issues. One or more issues have been detected with your storage. ...

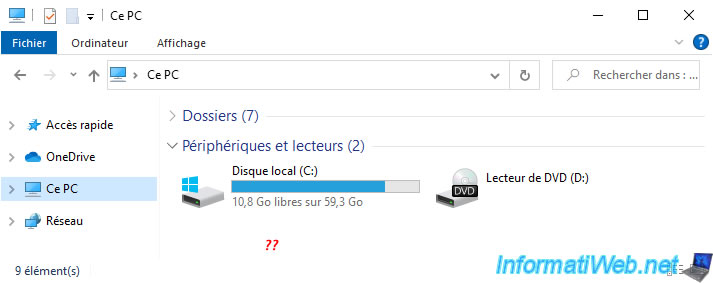
Obviously, in file explorer, your "RAID 5 storage" will be gone.
Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Windows 4/11/2022
Windows 10 - Delete an old network profile
-

Windows 10/10/2022
Windows 10 - Reset your PC
-
Windows 7/20/2021
Windows 8 / 8.1 - Refresh your PC (reinstall Windows only)
-

Windows 2/27/2017
WTG - Windows workspace on USB key

You must be logged in to post a comment