Create a storage space (software RAID: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 11) on Windows 8 to 11
- Windows
- Windows 8 / 8.1, Windows 10, Windows 11
- 13 March 2025 at 14:36 UTC
-

- 2/8
4. Simple storage space (RAID 0 software)
4.1. Create a simple storage space (RAID 0)
With Windows Storage Spaces, you can create a more efficient storage by using at least 2 physical disks.
In the background, Windows will create a software RAID 0 which consists of writing half of each data on the 1st disk and the other half of each data on the 2nd disk.
To create this type of storage, in the "Storage Spaces" window, click on the "Create a new pool and storage space" link.
Warning : in the event of a disk failure, you will lose all the data on this simple storage (software RAID 0), because you will end up with half of each data.
All the data will therefore be corrupted.
Note that creating storage spaces in Windows requires administrator rights since you will need to modify physical disks.
Click "Yes" when the "User Account Control" (UAC) window appears for the "Storage Spaces Settings" application.
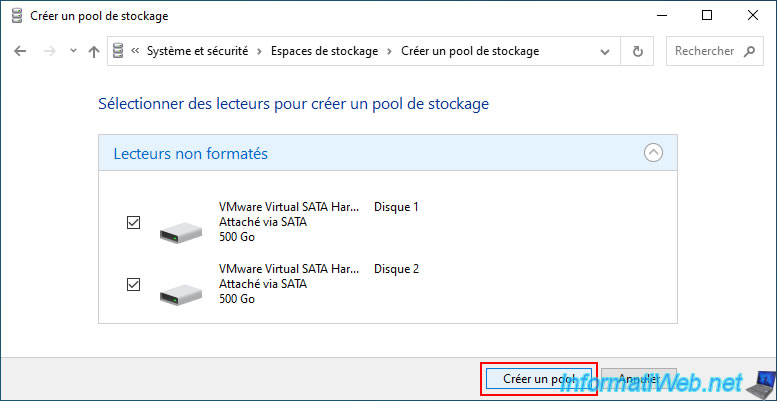
Select the disks to use and click "Create pool".
In our case, our 2 500GB disks that are blank.
As you can see, when you want to create a storage pool, Windows only displays unformatted drives.
If disks do not appear in this "Unformatted drives" list, refer to step "1. Blank disks required" of this tutorial to fix the problem.
Then, close this window and open it again.
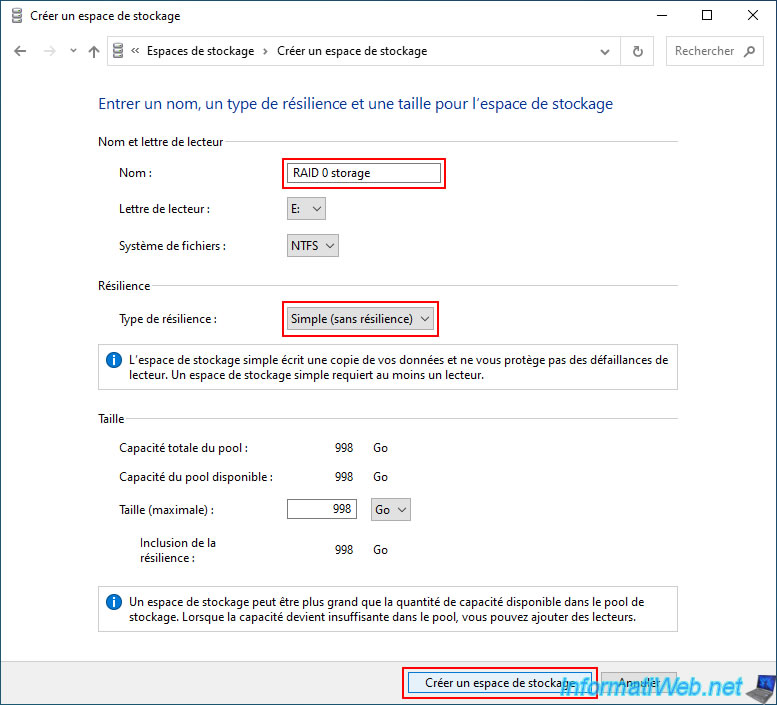
To create a storage space, you will need to indicate:
- Name: the name under which it will appear in the file explorer.
In our case: RAID 0 storage. - Drive letter: the letter that will be assigned to it in the file explorer.
By default, the next available letter in your case. - File system: the file system you want to use on this storage space.
Usually: NTFS. - Resilience type: the type of storage space you want to use.
In this case, we will use the "Simple (no resiliency)" resilience type which allows you to create a software RAID 0.
This allows you to create a more efficient storage (recommended for storing temporary files during video editing, for example), but whose data security is not important.
As indicated by Windows, this type of storage requires at least 1 drive (physical disk), although this is only of interest if you use at least 2 physical disks.
If you use a single physical disk, the performance will be exactly the same as the physical disk used. - Size: by default, the size indicated will be the maximum possible size (depending on the resilience type and the size of your physical disks).
Once your storage space is configured, click on "Create storage space".
Warning : as Windows tells you, the simple storage space does not protect you against drive failures.
In other words, if at least one physical disk in this storage space fails, you will lose all the data in this storage space.
Your new "RAID 0 storage" storage space of type "Simple (no resiliency)" appears.
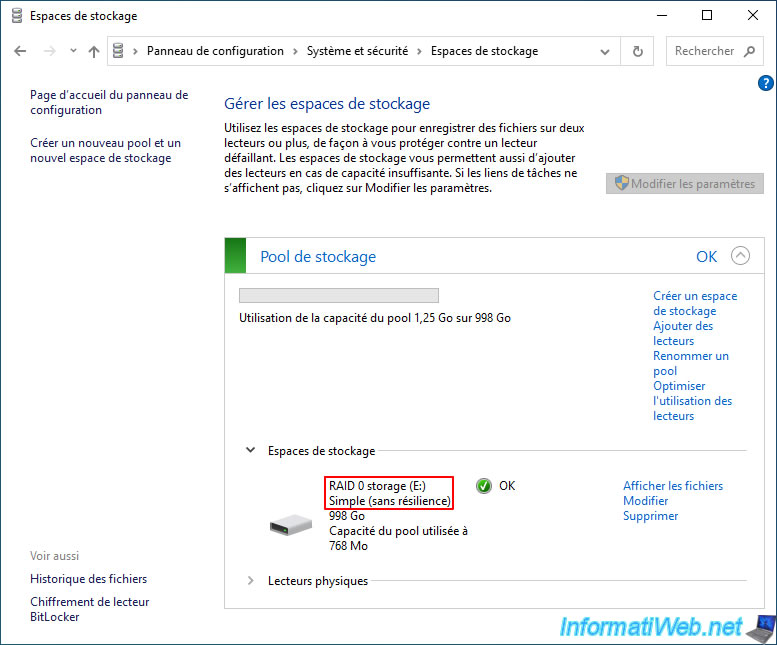
If you click on "Physical Drives" you will see the list of physical drives used for this storage pool.
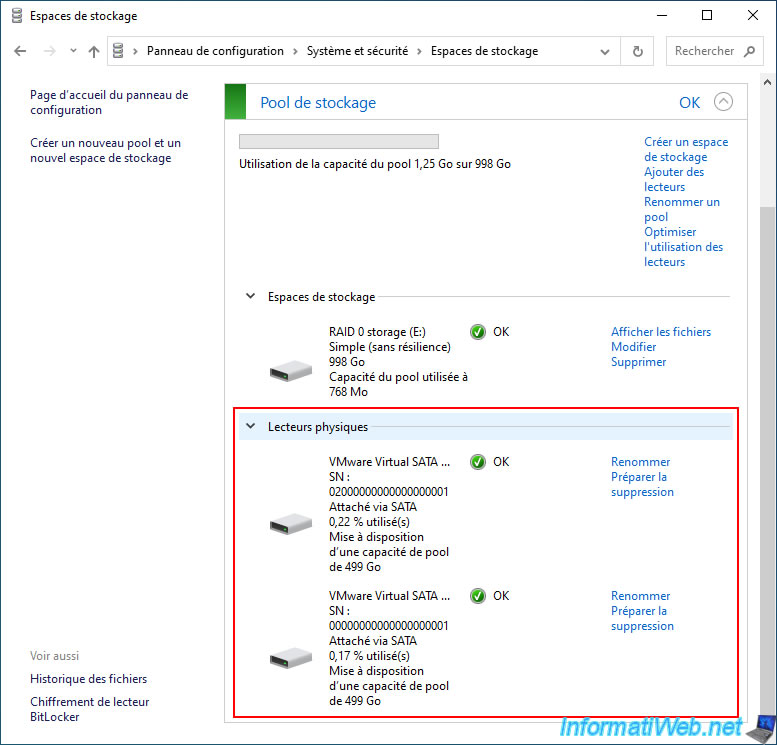
If you go back to Windows Disk Management (via a right click "Manage" on "This PC"), you will see this new storage space "RAID 0 storage" appear instead of the physical disks used by it.
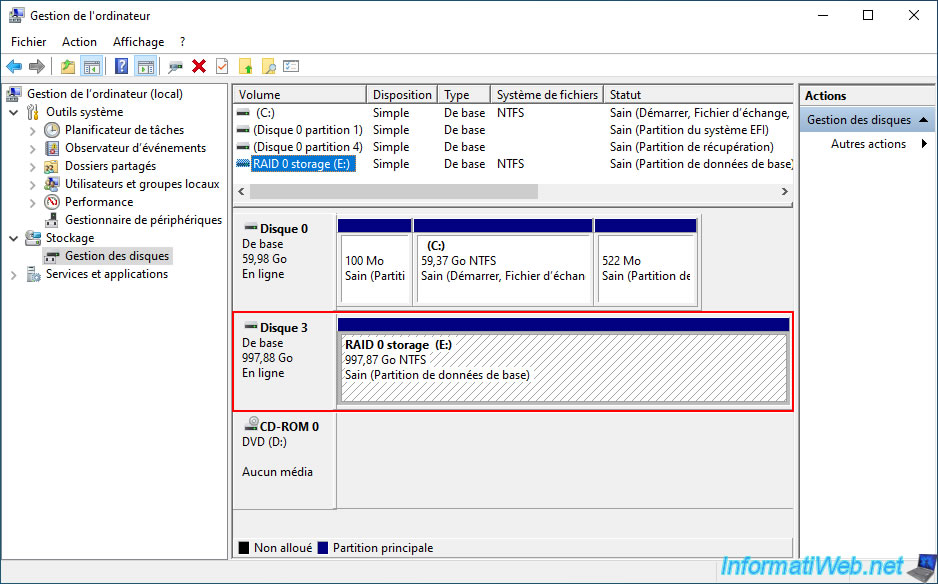
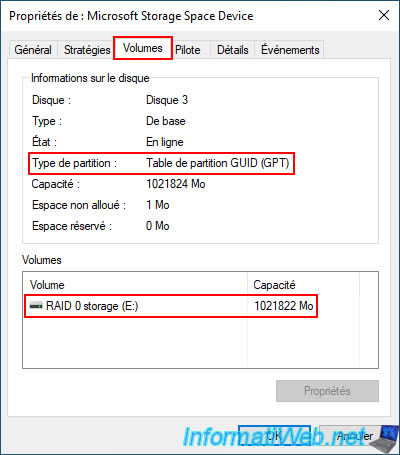
If you right click "Properties" on this disk you will see that it is a "Microsoft Storage Space Device".
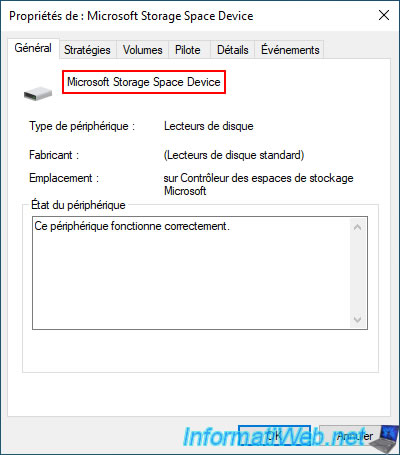
In the "Volumes" tab, you will see the name of your storage space appear (in our case: RAID 0 storage).
You will also see that Windows uses a GUID Partition Table (GPT) on storage spaces.
4.2. Data lost in case of physical disk failure with simple storage (RAID 0)
If a physical disk used for your simple storage fails, Windows will show you the notification below.
Plain Text
Check for storage issues. One or more issues have been detected with your storage. You may need to add or replace one or more drives.

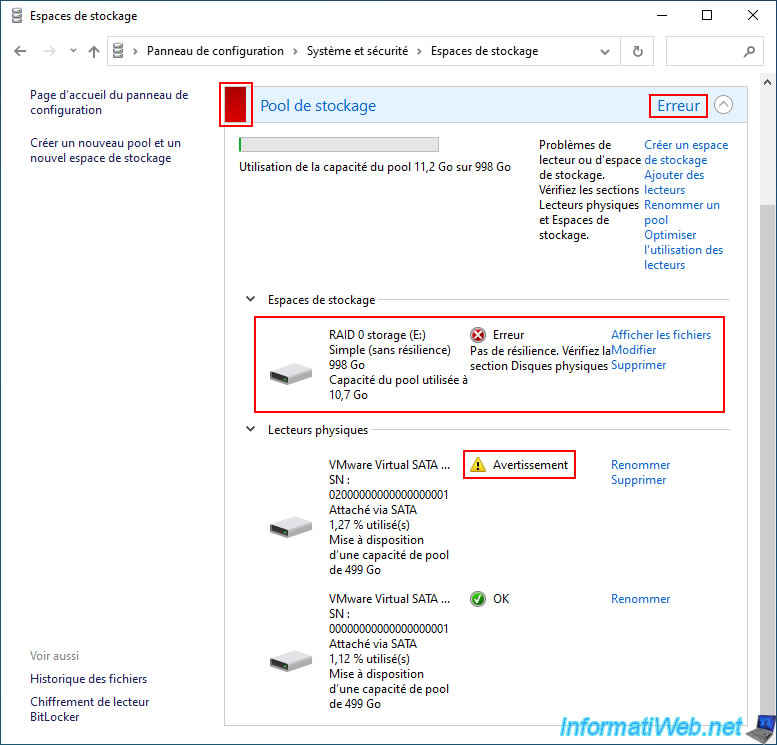
In the "Storage Spaces" section of the control panel, you will see that the status of your storage pool is "Error".
Plain Text
Drive or storage space problem. Check the Physical Drives and Storage Spaces sections.
Plain Text
RAID 0 - simple (no resiliency). Error. No resilience. Check the Physical drives section.
On Windows 8.1, the message will be a little different, but the problem remains the same.
Plain Text
Error. Inaccessible. Reconnect the drives.
Indeed, at least one of the physical disks used is causing problems.
In our case, the status of the 1st physical disk used is "Warning".
On Windows 8.1, the status of the physical disk may be "Warning. Disconnected. Reconnect the drive.".
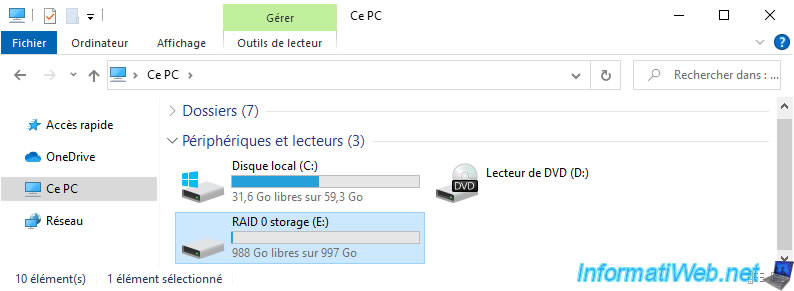
In explorer, your simple storage may still appear.
However, it is not really usable.
Note: on Windows 8.1, this will disappear.
If you go into this simple storage, you will see that the files appear correctly.
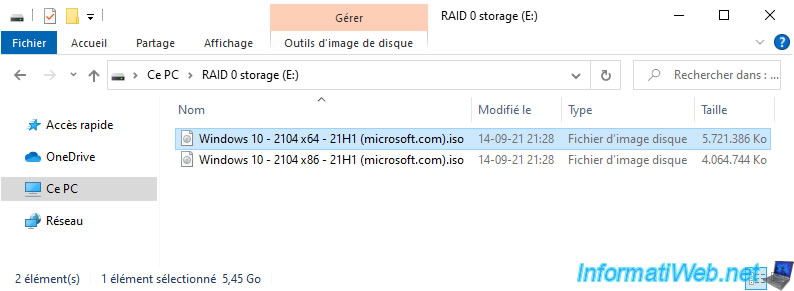
However, you will not be able to move or copy files that are there entirely to another location.
Indeed, since half of each data is missing, all visible files are therefore corrupted.
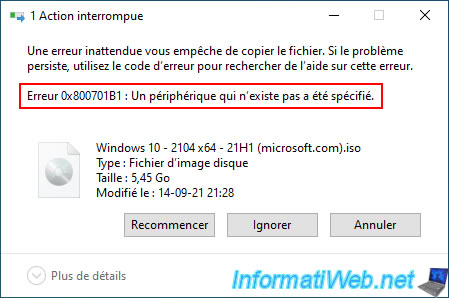
Hence the error below that will occur if you try to copy one of these files.
Plain Text
An unexpected error is keeping you from copying the file. Error 0x800701B1: A device that does not exist was specified.
If the disk with a "Warning" status is simply a physical disk that you had temporarily unplugged, simply plug it back in and Windows will detect it again.
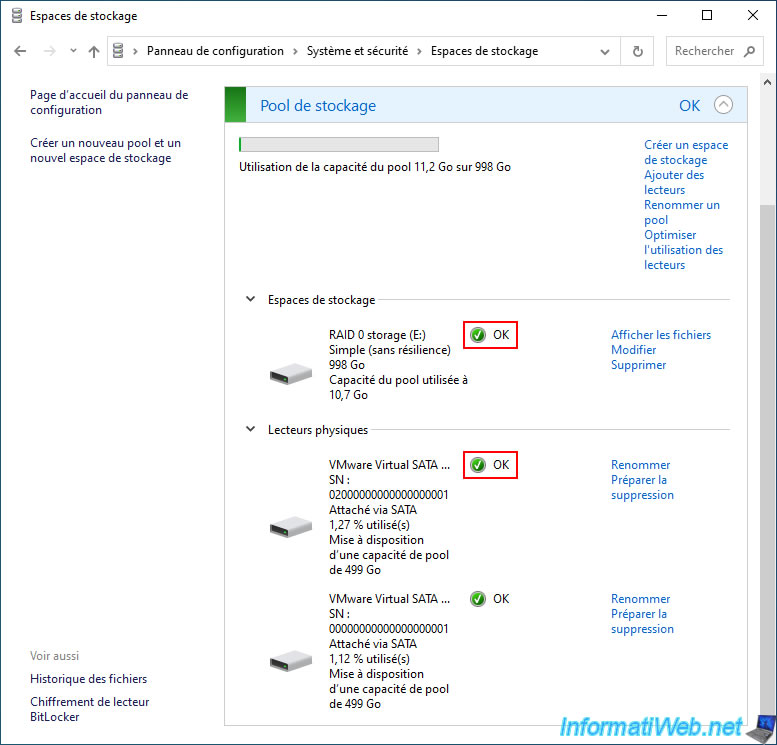
4.3. Delete a single storage space (RAID 0)
To delete a single storage space (RAID 0), click the "Delete" link to its right (in the "Storage Spaces" section).
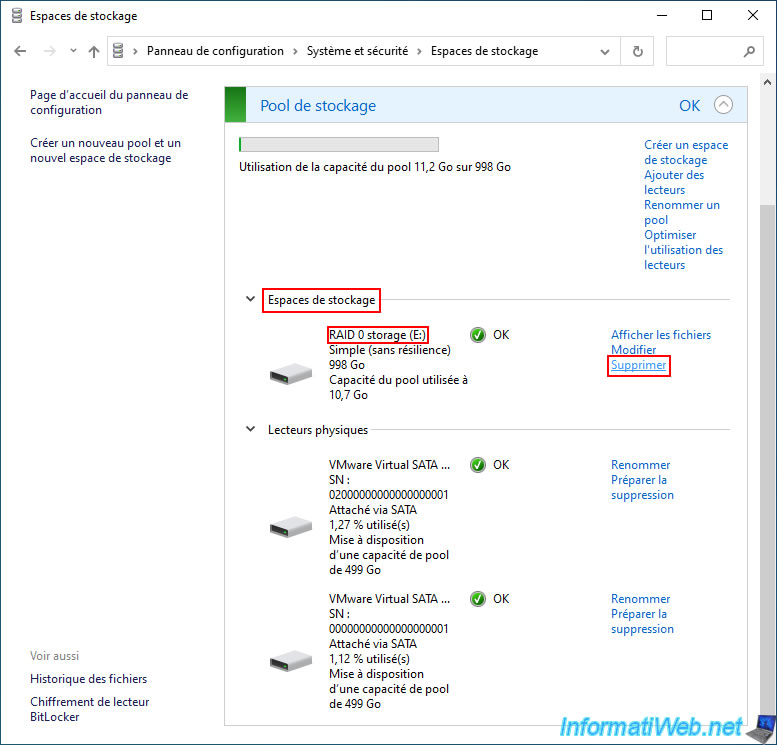
Windows warns you that all data on this simple storage space will be permanently deleted.
Click "Delete a storage space".
Plain Text
Deleting a storage space permanently deletes all the files that it contains. You can't recover the files by using the Recycle Bin.
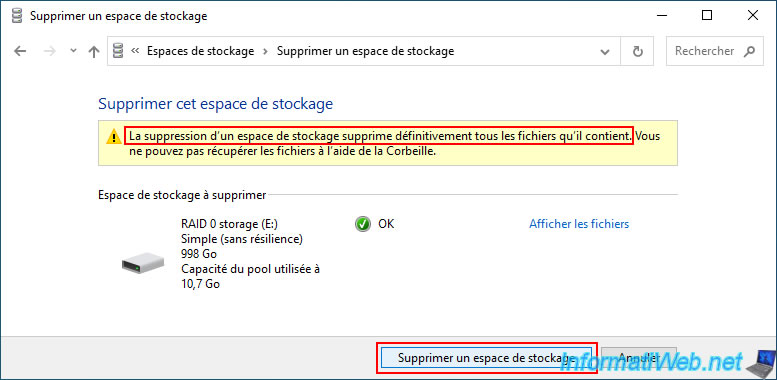
The desired simple storage space (RAID 0) has been deleted.
However, the storage pool (group of physical disks) on which it was located still exists.
Hence the fact that the previously used physical disks still appear in the "Physical drives" section.
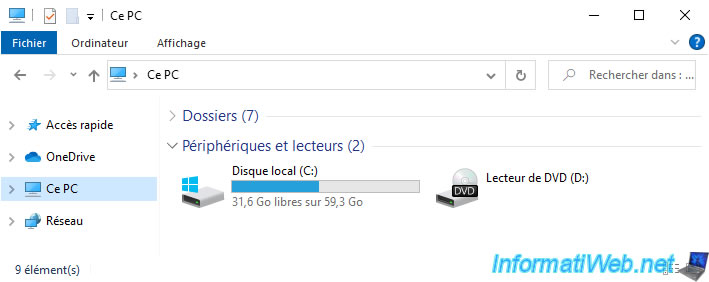
In file explorer, the storage space "RAID 0 storage" has disappeared since it was deleted.
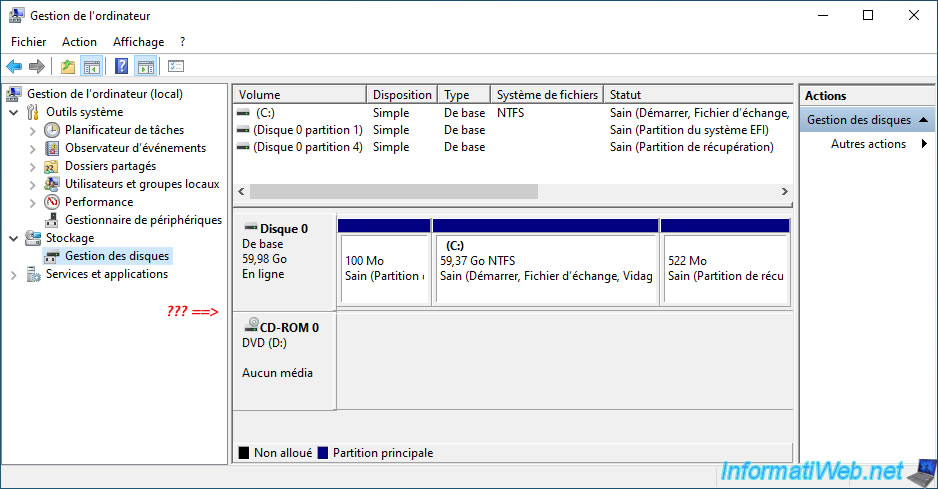
Important : if you look in Windows Disk Management, you will notice that your physical disks no longer appear there (despite the fact that the storage space has been deleted).
Indeed, to fix the problem, you will also have to delete the storage pool created previously as explained in the next step of this tutorial.
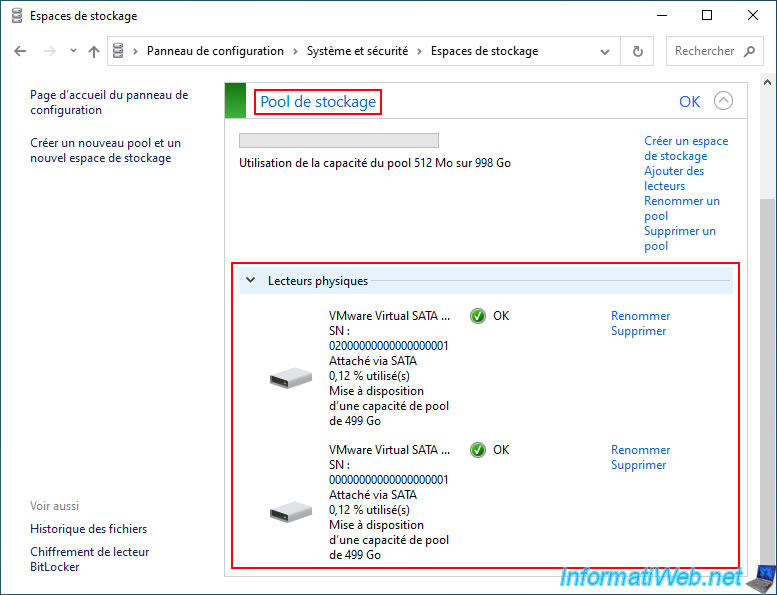
4.4. Delete a storage pool
To regain access to your physical disks, you also need to delete the storage pool that is still displayed in the "Storage Space" section of the Windows control panel.
To do this, click the "Delete pool" link for the desired storage pool.
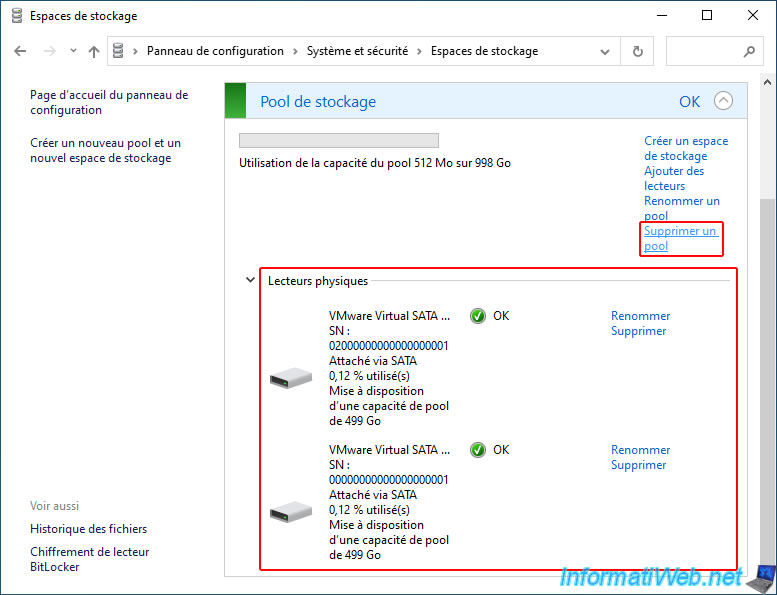
Confirm the deletion of this storage pool by clicking "Delete pool".
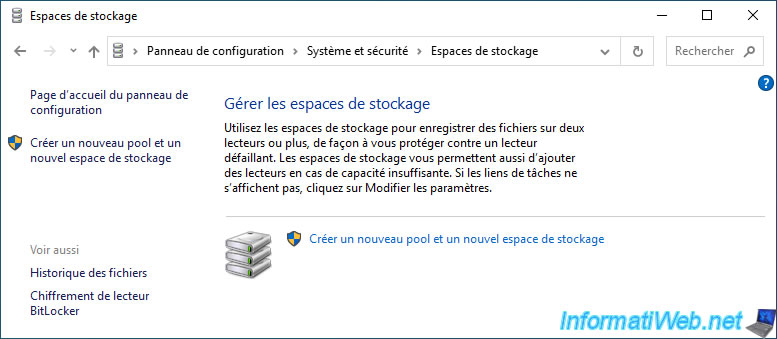
Now, the "Manage Storage Spaces" section is empty and you only see the default link "Create a new pool and storage space".
Share this tutorial
To see also
-

MultiBoot 7/1/2024
VHD/VHDX multiboot with Windows 10 and Windows 11
-

Windows 11/4/2024
Windows 11 - Use a Bluetooth headset
-
Windows 5/26/2021
Windows 8 / 8.1 - Recover the start menu
-

Windows 4/29/2016
Windows 8 / 8.1 / 10 / 11 - Startup repair
No comment