- Windows
- Windows 8 / 8.1, Windows 10, Windows 11
- 27 March 2025 at 14:10 UTC
-

Since Windows 8, you can create a three-way mirror storage spaces to permanently have 2 or 3 copies of your data using a software RAID 1 or 11.
In this tutorial, we used a "Three-way mirror" storage space. This means that your data is written 3 times on your physical disks.
Which, thanks to 5 physical disks, can support up to 2 physical disks failing simultaneously.
Tutorial made on Windows 10 version 2104 and also tested with Windows 11 v21H2, 8.1 Pro and 8 Pro.
- Create a three-way mirror storage space (RAID 11)
- Add a physical disk to expand your storage pool
- Increase the size of a three-way mirror storage space (RAID 11)
1. Create a three-way mirror storage space (RAID 11)
As explained previously, in Windows, you can create a "Three-way mirror" type storage space that allows you to write 3 copies of your data.
Which requires 5 physical disks (according to the background check performed by Windows and according to Microsoft's documentation) and not 3 physical disks as indicated by Windows (and visible in the image below).
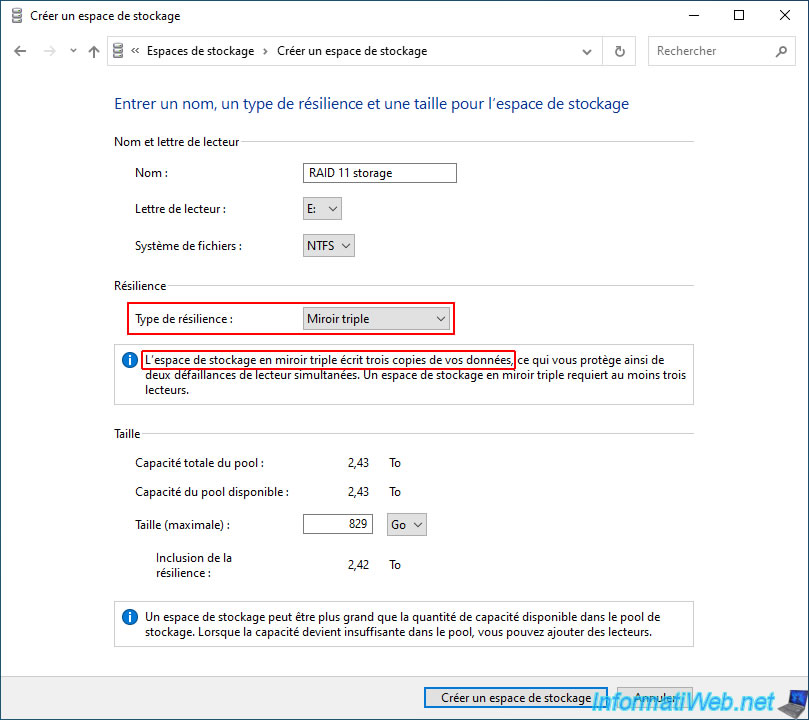
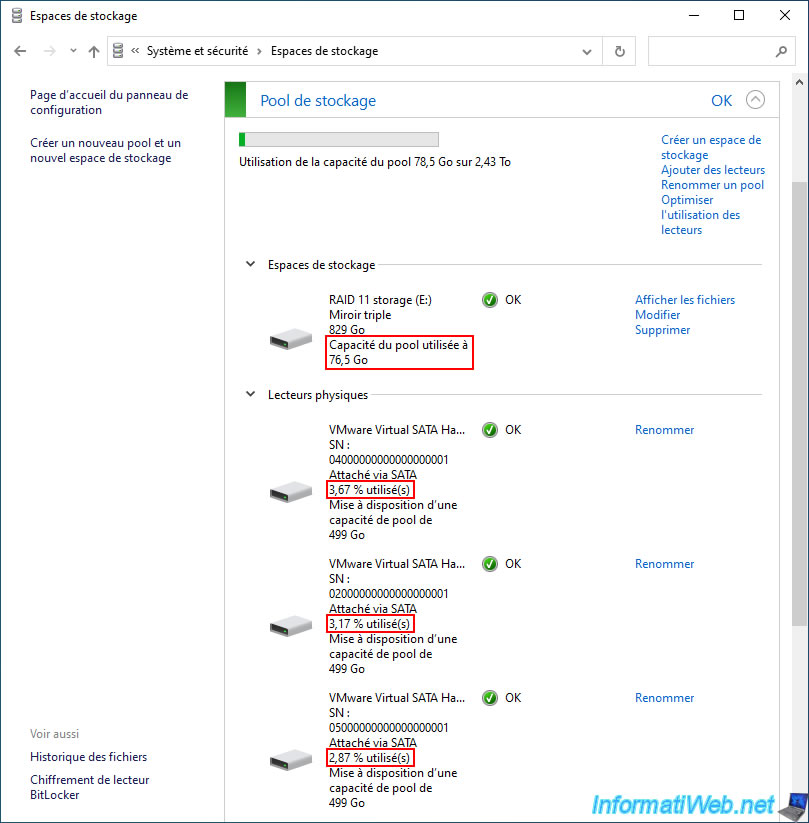
In our case, we created a "Three-way mirror" type storage space with 5 physical disks of 500 GB.
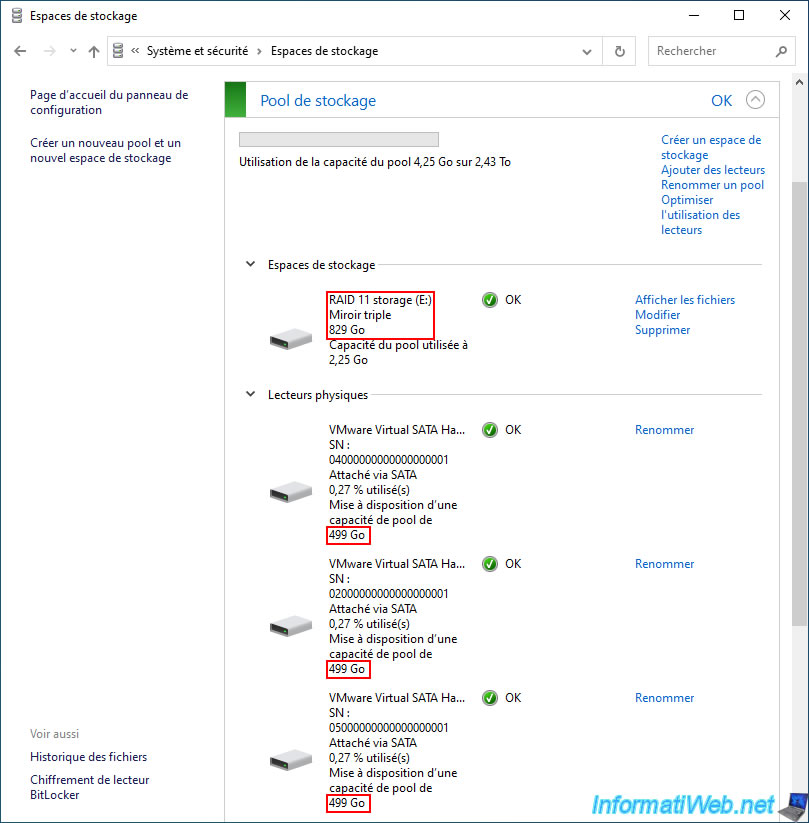
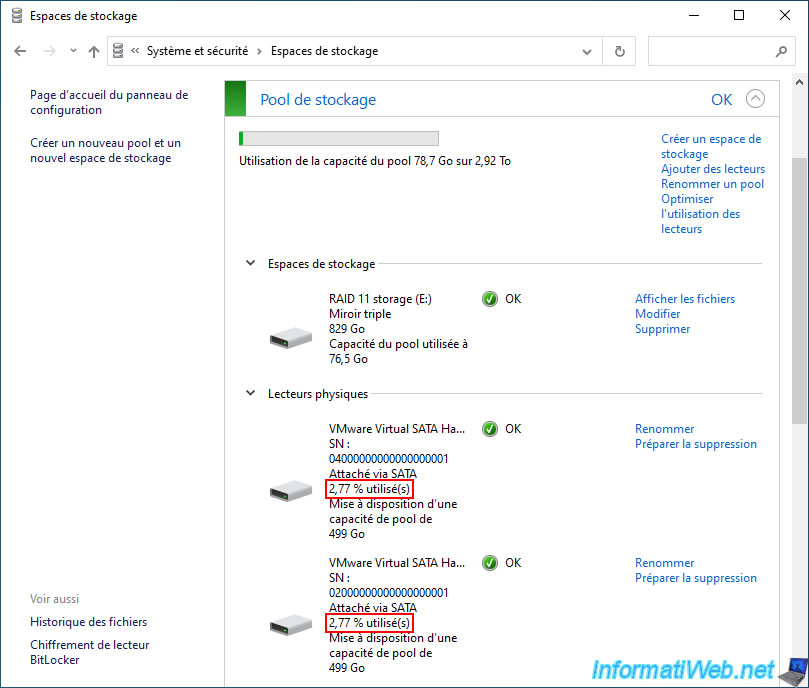
As you can see, in our case this storage space has a size of 828 GB at the moment.
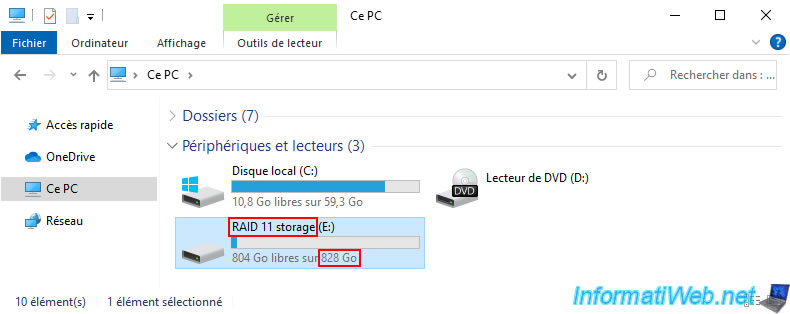
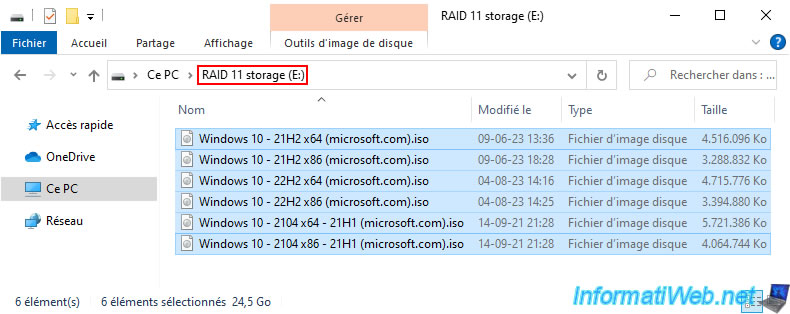
For testing, we stored 25GB of data in this "RAID 11 storage".
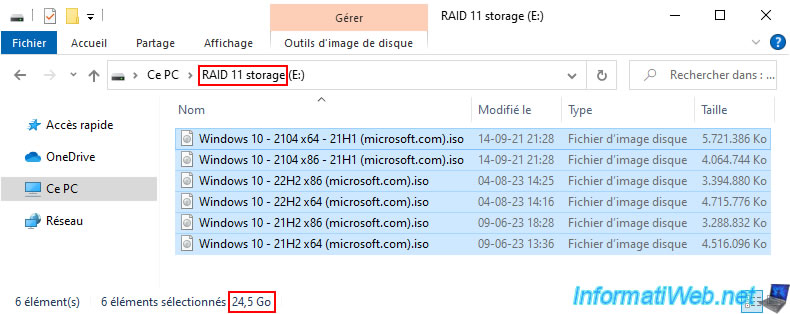
In the "Storage Space" section, we can see that the used pool capacity is 76.5 GB (approximately 3 x 24.5 GB of data).
Also, all disks are used more or less equally.
2. Add a physical disk to expand your storage pool
If you are running out of space on your "Three-way mirror" storage space, you can increase the available space on it by adding a physical disk to your storage pool.
To do this, first shut down your computer to plug in an additional physical disk to your computer, then turn it back on.
Then, go to the "System and Security -> Storage Spaces" section of the control panel to return here.
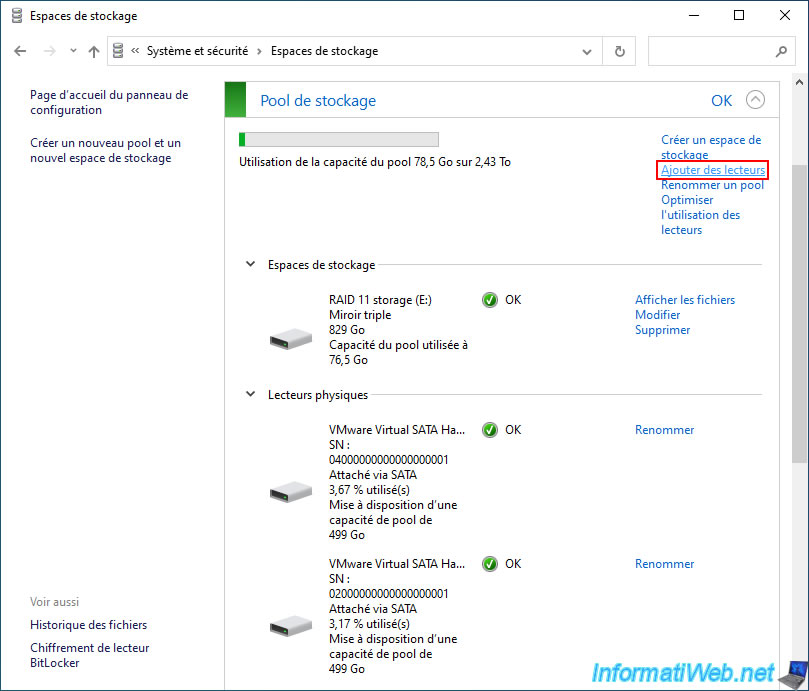
Click the "Change settings" button at the top so that the grayed out options become accessible and click the "Add drives" link.
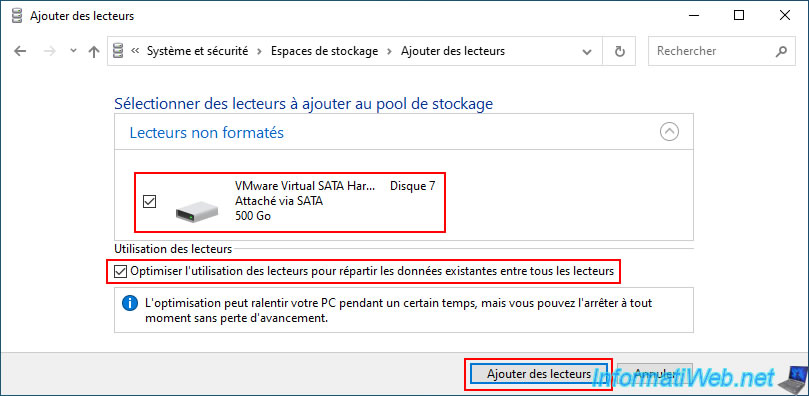
Check the box to the left of the new physical disk to add to your storage pool and preferably check the box "Optimize drive usage ...".
This will allow you to benefit from the best possible performance.
Then, click on the "Add drives" button.
Note: the "Optimize drive usage ..." option is not mandatory and is only available since Windows 10.
The message "Optimizing usage..." appears.
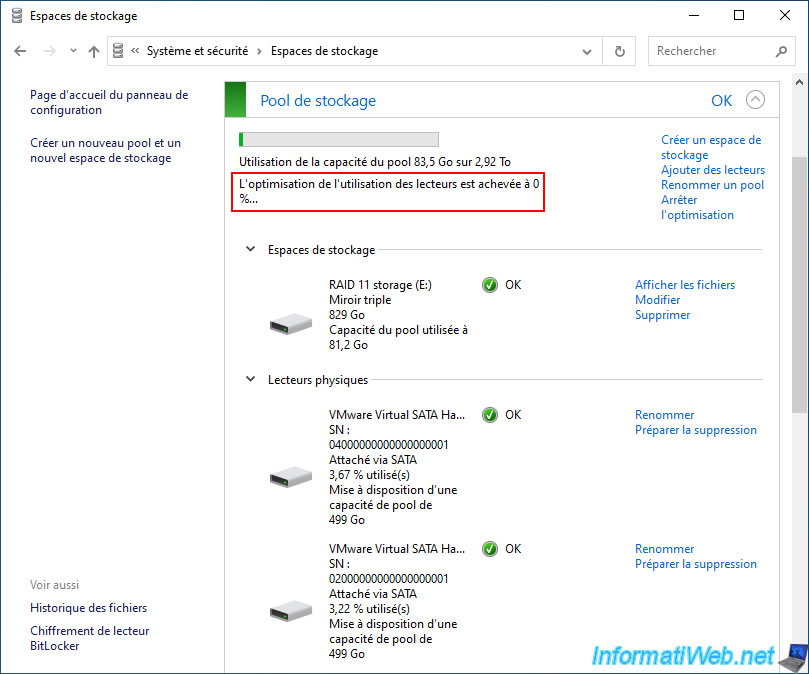
Right now, you can see that your new physical disk is used at about 0%.
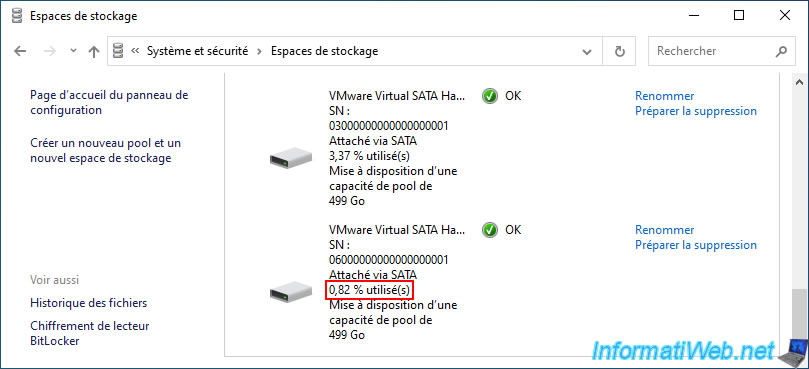
Over time, the utilization percentage of your new physical disk will increase and the utilization percentage of other physical disks in that same storage pool will decrease.
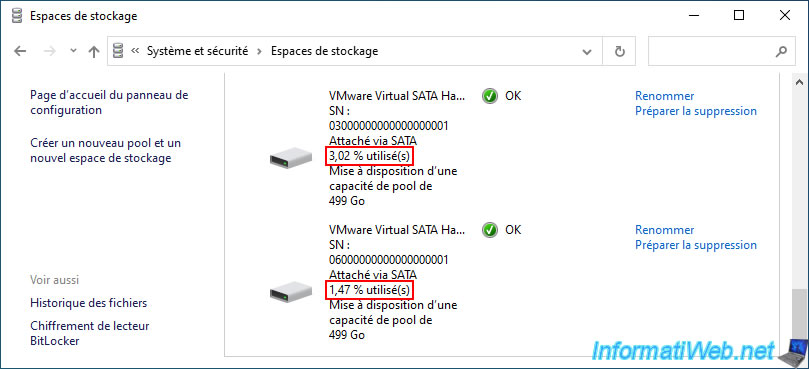
After drive optimization is complete, the utilization percentage of all physical disks in your storage pool will be similar or the same.
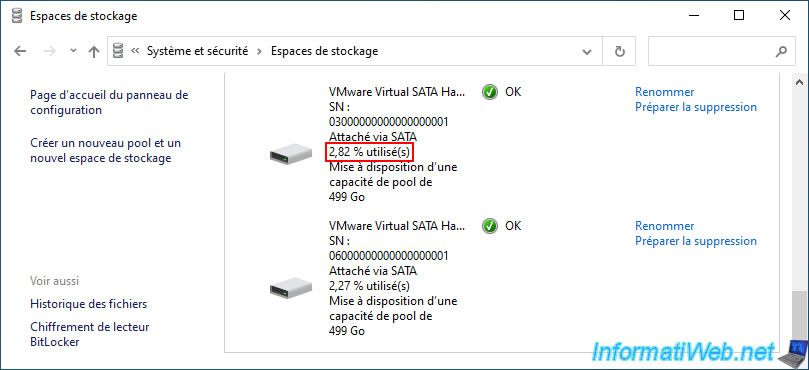
If you open file explorer, you will see that your "RAID 11 storage" storage size has not changed, despite adding a physical disk to your storage pool.
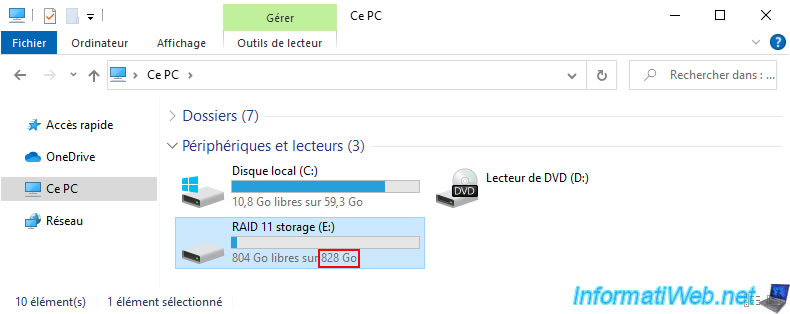
3. Increase the size of a three-way mirror storage space (RAID 11)
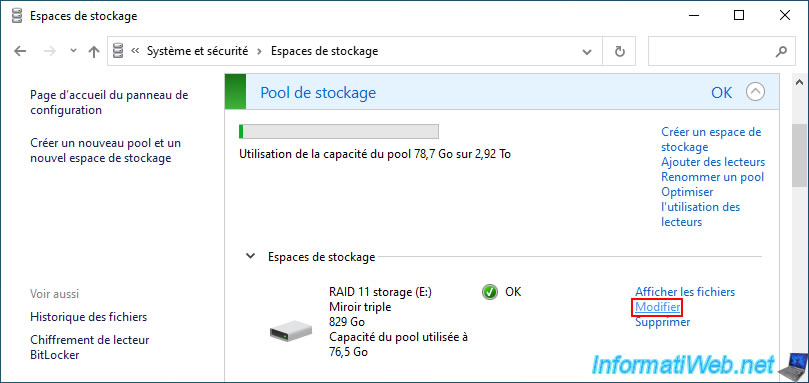
To change the size of your storage space in file explorer, you must change it manually from the "Storage Spaces" section of the control panel.
To do this, click on the "Edit" link located to the right of your "RAID 11 storage" storage space.
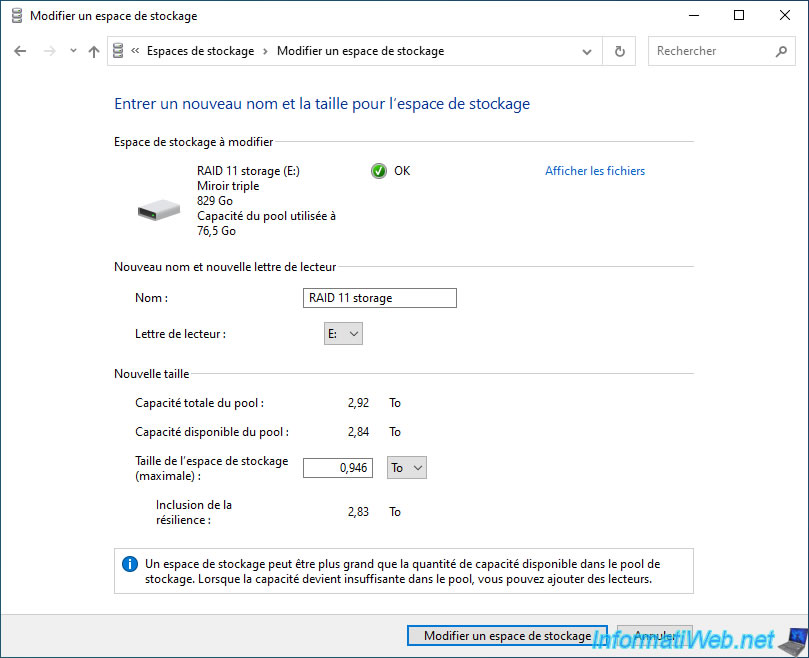
Currently, Windows reports the current size of your "Three-way mirror" storage space as "Storage space size (maximum)".
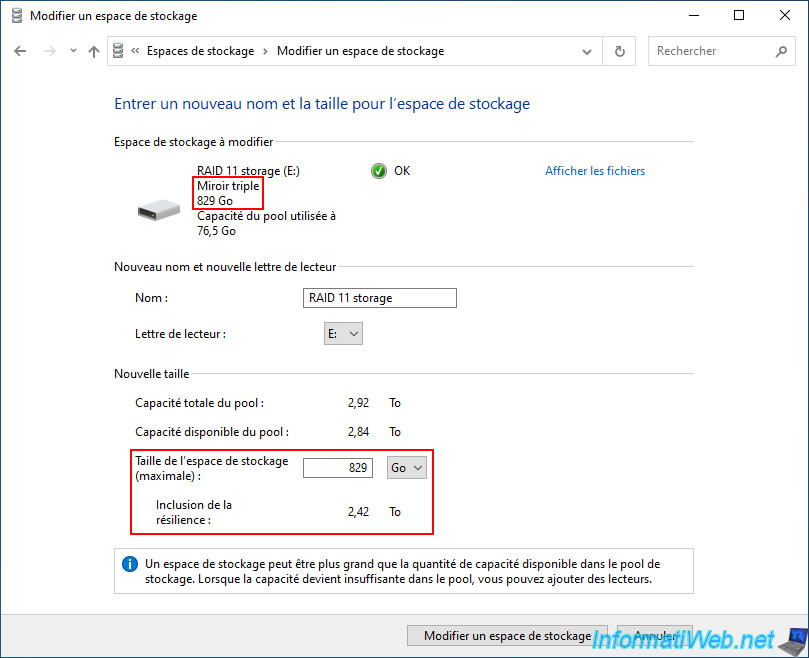
To avoid creating a storage space that would exceed the capacity of your storage pool (which is possible, but will require an additional physical disk when the time comes), the "Including resiliency" value must be lower than the "Available capacity of the pool".
However, you cannot directly modify the "Including resiliency" value.
You must therefore find the ratio used by Windows between the "Storage space size (maximum)" value and "Including resiliency".
To do this, the easiest way is to temporarily indicate "2" in the "Storage space size (maximum)" box.
With a "Three-way mirror" type storage space, you will probably see the value 6 appear for "Including resiliency".
To find the ratio you will need later, simply divide the "Including resiliency" value by the "Storage space size (maximum)" value.
Which gives in our case: 6 / 2 = 3.
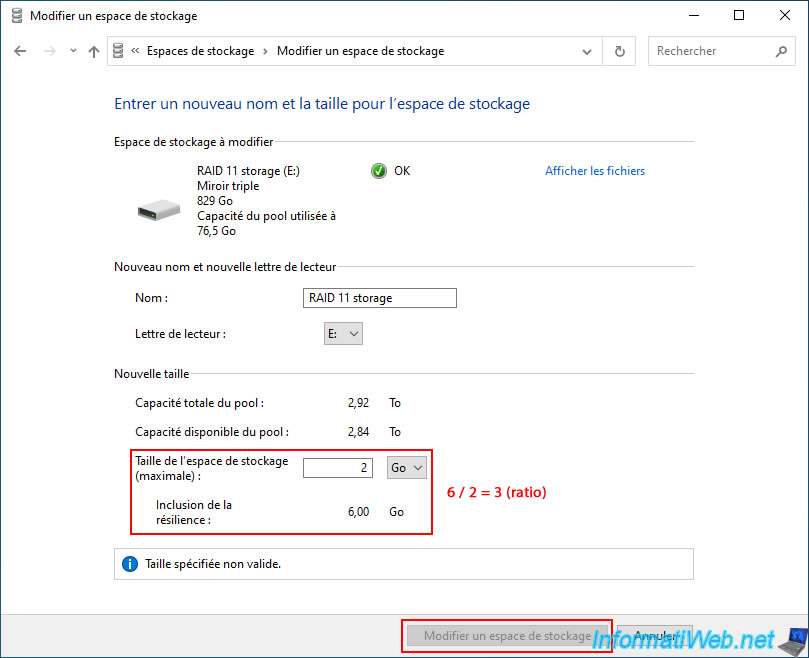
Now, divide the "Available pool capacity" value (in our case: 2.84 TB) by the ratio you just found (in our case: 3).
Which gives in our case: 0.946 TB.
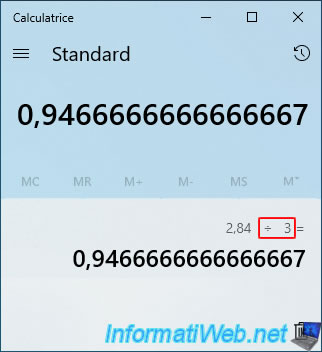
Enter the value found by keeping only 3 digits after the decimal point in the "Storage space size (maximum)" box.
Which gives in our case: 0.946 TB.
As expected, Windows tells us that the inclusion of resilience is worth 2.83 TB.
Which is very slightly less than the available capacity of our pool.
So, all the space available on our physical disks can be used for our data, as well as the parity data automatically written by Windows.
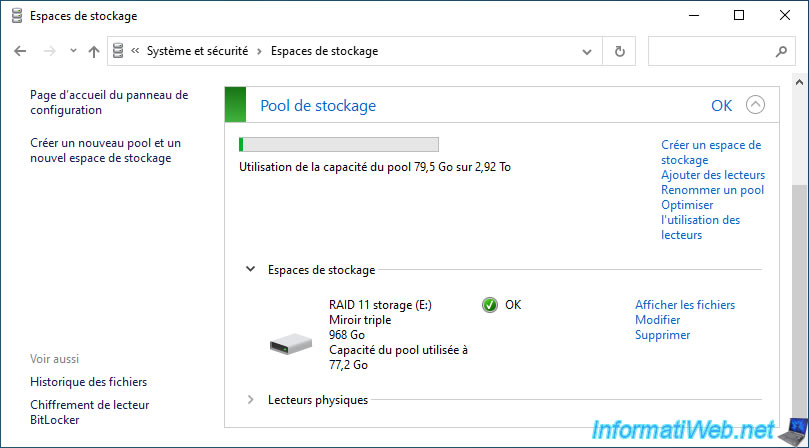
The size of our storage space has been modified.
However, we can see that Windows shows us a capacity of 968 GB instead of 0.946 TB in our case.
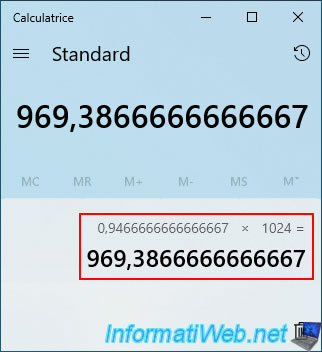
Which is quite normal, because 1 TB is worth 1024 GB and not 1000 GB.
Moreover, if we multiply the value in TB found previously (0.946... TB) by 1024, we actually find approximately 969 GB.
In file explorer, you will see that your storage space size has indeed been increased.
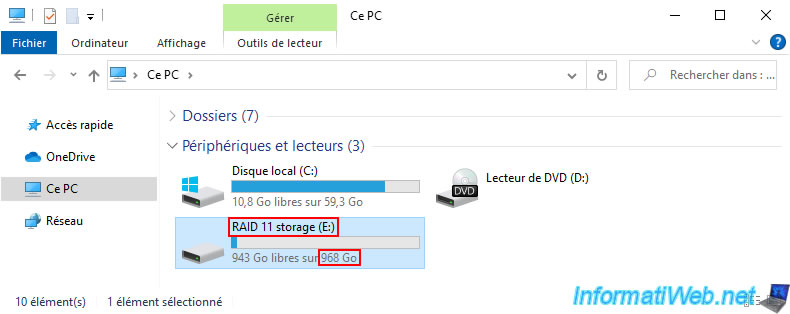
As expected, your storage data has been preserved.
Share this tutorial
To see also
-

Windows 7/10/2023
Windows 10 - Translate Windows using language packs (MUI)
-

Windows 10/28/2024
Windows 10 - Use a Bluetooth headset
-

Windows 10/30/2023
Windows 11 - Install Windows 11 v22H2 with a local account
-

Windows 3/26/2022
Windows 8.1 - Change a user's password

You must be logged in to post a comment